
Contents
In this article we will look at:
- What is alopecia or hair loss?
- The hair growth cycle
- What are the causes of alopecia/hair loss?
- What are the types of alopecia/hair loss?
- What are the symptoms of alopecia/hairloss?
- How is alopecia/hair loss diagnosed?
- What is the treatment for alopecia/hair loss?
- Hair Loss/Alopecia Treatment Related Topics
- In the Spotlight - Latest News on Hair Loss and Treatments
You can click on any of the links above to navigate to the section of your interest.
What is alopecia or hair loss?
Alopecia refers to any form of hair loss, hair thinning, or balding anywhere in the body. There are a variety of causes which can lead to hair loss, though the most common and natural one is ageing.
Hair loss often goes untreated, since it is not considered as a disease, besides regular hair fall is also a natural phenomenon. However, this can lead to unfortunate consequences, if the hair fall is more than normal.
On an average, one can lose between 80 - 100 hairs a day, of the 100,000 to 150,000 hairs on an adult head. There is a cause for concern if the hair loss is double than that.
Acute hair loss, or a sudden increase in hair loss, could occur due to many reasons such as stress, pregnancy in women, male pattern baldness, female pattern baldness, exposure to strong sunlight, anaemia, hypothyroidism’, vitamin B deficiency, autoimmune disorder, chemotherapy, etc.
Should you notice:
- loss of clumps of hair from your scalp
- excessive thinning of your hair
- unexplained loss of hair from any part of the body
- that you are tearing and pulling out your hair (Trichotillomania)
- incomplete hair loss on the scalp and/or eyebrows
you need to consult your family physician or a general practitioner immediately.
Depending on your condition, the general practitioner may direct you to a dermatologist, a trichologist, or even an endocrinologist if the hair loss is related to hormonal imbalance. You may also be referred to a psychologist if you suffer from Trichotillomania.
The Hair Growth Cycle
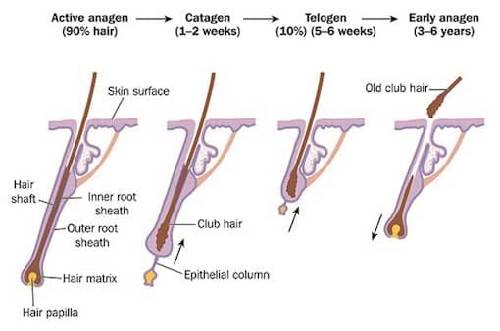
Hair is made up of keratin, which is a protein produced within the hair follicles on the uppermost layer of the skin. The follicles keep producing new hair cells and push out the old dead cells. The hair that you see on your head are compact strands made of dead keratinized cells.
At any given time, 90% or more of the hair on your scalp keeps growing. No two hairs have the same growth pace. In fact, each hair follicle goes through an entire growth cycle of its own, which is influenced by factors such as age, nutrition, illness, and also ethnicity.
It is because each hair follicle goes through a different growth cycle, that you shed only a certain number of hairs per day. If all the hairs on your head went through the same growth cycle, all your hair would fall off at once.
Between starting to grow and falling off, each strand of hair goes through three stages:
- Anagen (Growing Phase) - is the hair growing phase, which can last between two to seven years. At any time, about 80% - 90% of the hairs on your head are in the anagen phase. The hairs in this phase grow from one centimetre to half an inch every 28 days. Your genetics determine the amount of time your hair follicle stays in the anagen phase.
- Catagen (Regression Phase) - signals the end of the active growing phase and approximately 1% of the hair is in this phase at any given time. This phase of the hair lasts for around 10 to 14 days.
- Telogen (Shedding Phase) - this is a resting phase, at the end of which your hair is released and it falls out, i.e., the resting hair stays in the follicle till it is pushed out by the growth of a new anagen hair. At any given time, 10% - 15 % of all hairs are in the telogen phase. The follicle then remains dormant for 3 months and the whole process recurs again.
What are the causes of alopecia/hair loss?
Some of the most common causes of alopecia/hair loss include:
- physical stress due to overwork illness, accident, injuries, childbirth, emotional disorders, or surgery which can cause telogen effluvium
- usage of birth control pills by women
- pregnancy in women which can result in hormonal imbalances
- scalp infections such as ringworm or fungal infections
- poor diet, especially less protein intake, which can cause hair loss as hair strands are essentially made of the protein, keratin
- excessive hair styling and colouring
- smoking
- genetic hair loss
- autoimmune disorders such as Alopecia areata, or lupus, where the immune system of the body attacks its own healthy cells, including hair follicles
- chemotherapy which can result in spot baldness or complete baldness
- taking excessive amounts of Vitamin A supplements
- male pattern baldness caused by a combination of family genes and male hormones
- female pattern baldness caused by family genes
- medical conditions such as, anaemia, iron deficiency, polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) in women, eating disorders, and thyroid disease
- vitamin B deficiency in the body
- sudden weight loss due to physical trauma
- burns and X-rays too can cause sudden temporary hair loss
- taking medicines such as blood thinners and anti-depressants
- trichotillomania which is an impulse control disorder causing people to compulsively pull out their own hair
- natural ageing, especially when people enter their 50s or 60s.
What are the types of alopecia/hair loss?
When your hair growth cycle is disturbed, problems such as hair loss, and hair thinning begins. If for instance, your hair enters the resting phase too early, excessive shedding and thinning of the hair occurs.
There can be a number of reasons which lead to the disruption of the hair growth cycle, and result in different types of alopecia such as:
- Alopecia areata - starts suddenly and causes hair loss in patches anywhere in the body in children and young adults. This condition is also known as ‘spot baldness’. This condition is observed to run in families and experts believe this condition could be the result of autoimmune disease, where the immune system of the body mistakenly attacks the hair follicles.
A person suffering from this condition may lose all the hair. This though can be a temporary condition and the hair may grow back after a few years. Though there is no guarantee.
- Involutional alopecia - is a natural process, wherein, hair thinning occurs with age. With ageing, most of the hair follicles go into the dormant or resting phase, while the length of the rest of the hairs gradually become shorter and as a result, the hair quantity becomes thinner.
- Androgenic alopecia - is a genetic condition. Men with this condition suffer from what is commonly known as male pattern balding, which can start during late teens or their early 20s. Women with this condition suffer from what is known as female pattern balding and begin to notice the thinning of their hair after around 40 years of age.
- Alopecia totalis - is an autoimmune disorder and occurs when a person experiences total loss of hair on the head, and face, including eyebrows and eyelashes. This can be a sudden process or a gradual progression of alopecia areata. This condition can affect children as well as adults.
- Alopecia universalis - is also an autoimmune disorder in which there is total hair loss all over the body, including eyebrows, eyelashes, and pubic hair. It is considered to be the most severe form of alopecia areata.
- Scarring alopecia - can be caused by various disorders such as:
- frontal fibrosing alopecia (occurs in women during menopause),
- scleroderma (an autoimmune rheumatic disease)
- lichen planus (an itchy rash),
- discoid lupus (a mild form of lupus)
- folliculitis decalvans ( occurs in men causing patchy baldness and scarring)
Scarring alopecia occurs mostly in adults and is a condition where the hair follicles get destroyed. The hair can never grow back.
- Trichotillomania - is a psychological disorder affecting mainly children who tear and pull out their hair. This can destroy hair follicles and prevent hair from growing.
- Telogen effluvium - occurs mainly due to the body’s reaction to stress, brought about by, illnesses such as cancer, mental and emotional disturbances, medications such as blood thinners, hormonal imbalances, stress during childbirth and so on. In this condition hair thinning occurs on the scalp. The hair usually regrows after the stress period is over.
- Alopecia barbae - is loss of facial hair and affects men, specially as it causes hairless patches in beards.
- Alopecia mucinosa - also known as follicular mucinosis is an autoimmune disorder. It causes inflammation of the hair follicles which can result in scarring or non-scarring hair loss. This condition can affect any part of the body and can affect both children and adults. If treated early, the hair will grow back. If the condition is too severe, the hair will not grow back.
- Traction alopecia - is a condition of hair loss which is common in women. It occurs due to tension in the hair shafts caused by very tight ponytails, braids, or pigtails. If the hair is tied regularly for too long, it can lead to prolonged traction alopecia, and the hair on the affected areas may never grow back.
- Anagen effluvium - is widespread hair loss all over the body due to chemotherapy, immunotherapy, or radiotherapy. The hair loss is usually temporary and grows back after a certain period of time.
What are the symptoms of alopecia/hairloss? How is alopecia/hair loss diagnosed?
The symptoms of alopecia or hair loss include:
- excessive hair loss ( more than 150 hairs a day) from the scalp
- hair loss from other parts of the body, apart from your head
- thinning of hair on the head, especially scalp
- a receding hairline
- patches of broken hairs
- an M shaped pattern in front of your head, just above your forehead, leaving the crown of the head exposed
- clumps of hair on your pillow
- complete loss of all hair from the head
- complete loss of all hair on the entire body
- excessive hair loss while shampooing
Diagnosis
Your doctor will ask you your medical history, your family’s medical history, and especially about hair loss in the family. By looking at your symptoms, and examining a few of your hairs under a microscope the doctor will be able to diagnose if it is a case of alopecia areata.
He may also perform a scalp biopsy to rule out the possibilities of fungal, ringworm or other infections.
Your doctor may also suggest a blood test to determine if the cause of hair loss is an autoimmune disease or hormonal imbalance.
What are the complications of alopecia/hair loss?
The complications of hair loss or alopecia are mainly psychological in nature. Hair loss can affect you emotionally, and cause you to feel that your identity is being threatened since it has to do with your self-image that you want to portray to others.
If you are suffering from excessive hair loss, it is not only advisable to undergo treatment immediately for it, but also to undergo counselling and talk therapy, which will not only help you manage your symptoms, but also boost up your self image, self confidence and help you to wholeheartedly accept yourself as you are.
Some complications of alopecia include:
- low self-esteem
- depression
- dandruff, if the alopecia is a result of poor nutrition
- sunburn on the scalp and exposure to the harmful ultraviolet rays of the sun, which can be prevented by wearing a hat or applying a sunscreen lotion on the scalp
- thyroid disease, diabetes, and vitiligo if a person suffers from alopecia areata since these conditions are also linked to problems with the immune system
What is the treatment for alopecia/hair loss?
Medical treatments
Depending on your gender, the type of hair loss or alopecia, and your overall health condition your doctor may prescribe intake of certain medications or even creams and ointments for application.
He may also suggest steroid injections, or treatments such as immunotherapy, hair transplantation, laser phototherapy, and UV Light treatment.
Alternative treatments for hair loss
There are alternative treatments available for hair loss too, such as aromatherapy, massage, acupuncture. Their efficacy, however, has not been tested.
An Ayurvedic treatment called Shirodhara however, has shown a certain amount of promise for stopping hair loss and aiding hair growth.
Hair Loss/Alopecia Treatment Related Topics
People interested in this topic also read:
- Hair Fall Treatment Procedures
- Hair Transplantation Procedures Overview
- Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT)
- Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE)
- Scalp Reduction Surgery
- Artificial/Synthetic Hair Implant
- Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy for Hair Growth
In the Spotlight
Here are some latest news on hair loss:
Histogen Treatment for Female Hair Loss Cleared for Clinical Testing
Are Fad Diets Causing Excessive Hair Loss? Read This!
Pattern hair loss could be due to gut bacteria
Patient Experiences



Questions answered by trusted doctors

Regards
Dr. Omkar Balkrishna Shahapurkar
Pune


Did you know?
More than half the male population suffers from hair loss
58% of the male population in India, aged 20-50 years, has AGA (Male Androgenetic Alopecia).
Reasons for hair fall
According to hair specialists the four major hair fall reasons in India are, stress, bad habits, pollution, and unhealthy eating.
Men vs women distribution
Compared to men, women have severe hair loss issues, mostly due to their health conditions.
Related videos
Related articles
Dialysis is a procedure in which the blood is filtered mechanically without the help of the kidneys. If the kidneys are not functioning properly then Dialysis will take over the function of the failed kidneys.
Hair transplantation is a surgical method, which is used to treat varying levels of alopecia in men and women. Know more about Hair Transplant, Alopecia, Hair fall treatment and other useful facts, links and videos on Health-Wiki | Practo
Artificial or synthetic hair implantation procedure is performed by qualified and seasoned physicians using hair implant devices. To know about the method, cost, and side effects of artificial hair implant goto Practo Procedure-Wiki.



