
Contents
In this article we will look at:
- What is meningitis?
- How does meningitis occur?
- Who is prone to meningitis?
- What are the causes of meningitis?
- What are the symptoms of meningitis?
- How is meningitis diagnosed?
- What are the complications of meningitis?
- What is the treatment of meningitis?
You can click on any of the links above to navigate to the section of your interest.
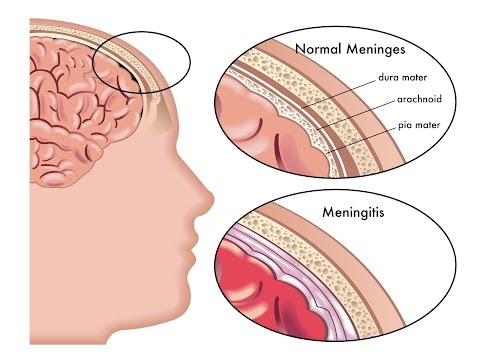
What is meningitis?
Meningitis is an inflammation of the meninges. The meninges are the three tough layers of protective tissue that cover the brain and spinal cord. Meningitis can occur when the fluid surrounding the meninges becomes infected.
If not treated, meningitis can cause brain swelling and permanent disability, coma, and even death.
How does meningitis occur?
Meningitis is usually caused by a viral or bacterial infection. Fungal meningitis is very rare and is caused by fungus spreading through blood to the spinal cord.
Viral meningitis is the most common form of meningitis, followed by bacterial meningitis.
Identifying the cause of meningitis is the key to treating it. Bacterial meningitis can be life-threatening.
Bacterial meningitis: There are several strains of bacteria that can cause meningitis:
- Pneumococcal bacteria: this usually affects people with a weakened immune system, especially babies.
- Haemophilus influenzae type b (Hib) bacteria: which is responsible for severe pneumonia, meningitis and other invasive diseases almost exclusively in children aged less than 5 years.
- Meningococcal bacteria: of which there are several different types, called A, B, C, W, X, Y and Z. This form bacteria causes serious infection of the meninges (the three membranes which line the skull and vertebral canal and envelope the brain and spinal cord.) that affects the brain membrane. It can cause severe brain damage and is fatal in 50% of cases if untreated. This may be caused by an ear or sinus infection, a skull fracture, or, rarely, after some surgeries.
- Listeria monocytogenes (listeria): which can be found in unpasteurized cheeses, hot dogs and luncheon meats. People with weak immune systems are most susceptible to this bacteria such as pregnant women, newborns, older adults. An infection during late pregnancy may be fatal to the baby.
Viral meningitis: This is the most common and least severe among all the types of meningitis. Viral meningitis is usually mild and often clears off by itself. Viruses such as herpes simplex virus, HIV, mumps, West Nile virus and others also can cause viral meningitis.
Viruses in the Enterovirus category cause 85 percent of cases. The different types are:
- enteroviruses: which cause 85 % of viral meningitis cases.
- the mumps virus: around 1 in 1,000 people develop viral meningitis from mumps.
- the herpes simplex virus: a virus that usually causes cold sores or genital herpes.
Fungal meningitis
Fungal meningitis is meningitis caused by fungal infection. Fungal meningitis is relatively uncommon and can cause chronic meningitis, though it is not contagious. Its symptoms may mimic acute bacterial meningitis.
Though anyone can contract fungal meningitis, people with weakened immune systems, such as those suffering from HIV infection or cancer, are at greater risk.
Cryptococcal meningitis is a common fungal form of the disease and can be life-threatening
if not treated with an antifungal medication.
Other causes of meningitis
Chemical reactions, drug allergies, some types of cancer and inflammatory diseases such as sarcoidosis can also be the non-infectious causes of meningitis.
Who is prone to meningitis?
Anyone can potentially get meningitis, but it's more common among:
- babies and young children
- teenagers and young adults
- elderly people
- people with a weak immune system such as those with HIV, cancer, and people undergoing chemotherapy
What are the causes of meningitis?
The main causes of meningitis include:
- bacterial infection
- viral infection
- fungal infection
- through sexual contact and kissing
- through eating food which is contaminated with Listeria monocytogenes bacteria
- through coughing and sneezing which is how the bacteria can spread to nearby people
- through contact with infected blood
- during childbirth when a mother can pass germs that cause meningitis to her baby even if the mother doesn't have symptoms
- though stool could have enteroviruses or certain types of bacteria in it. Most of the time children contract meningitis this way. Thoroughly washing hands after a visit to the toilet could lessen the possibility of infection
What are the symptoms of meningitis? How is meningitis diagnosed?

The signs and symptoms that may occur in anyone older than the age of 2 includes:
- sudden high fever
- a severe headache that isn't easily confused with other types of headache
- stiff neck
- vomiting or nausea
- headache
- confusion or difficulty concentrating
- seizures
- sleepiness or difficulty waking up
- sensitivity to light
- lack of interest in drinking and eating
- skin rash in some cases, such as in meningococcal meningitis
Diagnosis
A general physician or a primary care doctor is the first go to the doctor in case of the appearance of symptoms of meningitis. A general physician can diagnose as well as prescribe the treatment. In the case of a child, a paediatrician needs to treat the child. In case of severe symptoms the general physician may refer you to an infectious diseases specialist or a neurologist.
The general physician or paediatrician can diagnose meningitis based on your medical history, a thorough physical exam and certain diagnostic tests.
During the exam, your doctor may check for signs of infection around the head, ears, throat and the skin along the spine.
Some tests your doctor may ask you to undergo include:
- Imaging: X-rays and/or CT scans can show may show swelling or inflammation in and around the head, may show infection around the chest or sinuses may which may be associated with meningitis.
- Blood cultures: Blood samples are taken in this test and then studied under a microscope for bacteria.
- Lumbar Puncture: which is also called spinal tap is a method to collect cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) and test if there is low sugar (glucose) level along with an increased white blood cell count and increased protein.
What are the complications of meningitis?
Complications of meningitis include:
- encephalitis
- persistent fever
- seizures
- syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone
- brain damage
- mental retardation
- partial or total paralysis
- partial or total speech loss
- cerebral palsy
- partial or total hearing loss
- behavioural and personality changes
- partial or total vision loss
What is the treatment of meningitis?
The treatment of meningitis will differ according to the type and cause of meningitis, whether bacterial, fungal, viral and other causes. The doctor may start may start antiviral and antibiotic treatment while the cause is determined.
During the course of the treatment, the doctor may drain any infected sinuses or mastoids (which are the bones behind the outer ear that connect to the middle ear.).
Questions answered by trusted doctors

Did you know?
Causes of meningitis
Meningitis can be caused by bacteria (40%), viruses (45-50%), tuberculosis (5%) and rarely parasites.
Meningitis in children
This is a dreadful condition affecting about 90,000 patients each year in India and especially children are affected in large numbers.
Non-Infectious causes of meningitis
Chemical reactions, drug allergies, some types of cancer and inflammatory diseases such as sarcoidosis can also be the non-infectious causes of meningitis.
Related videos
Related articles
A wart is a small growth which is flesh-colored, tan, pink, or white and feels like a grainy bump on the skin. Know more about Warts Infection, its causes, symptoms, treatment and other useful facts, links and videos on Health-Wiki | Practo
HIV stands for Human Immunodeficiency Virus. Know more about HIV, its causes, symptoms, treatment and other useful facts, links and videos on Health-Wiki | Practo
Psoriasis is a persistent inflammatory skin disorder, it is characterized by red skin covered with whitish scales. Know more about Psoriasis, its causes, symptoms, treatment and other useful facts and links and videos on Health-Wiki | Practo





I can understand your concern.
Who diagnosed it as meningitis?
Take her to any good hospital near you .
Treatment started the earlier the better.
You can consult any neurologist and a MD consultant physician in person for further evaluation and management.
Best regards.
Dr. Anil Kumar Jain.
Bangalore.