Contents
In this article we will look at:
- What is scabies?
- What causes scabies?
- Who is at a risk of contracting scabies?
- What are the symptoms of scabies?
- In which parts of the body do the symptoms of scabies appear?
- How is scabies diagnosed?
- What are the complications of scabies?
- What is the treatment of scabies?
You can click on any of the links above to navigate to the section of your interest.
What is scabies?
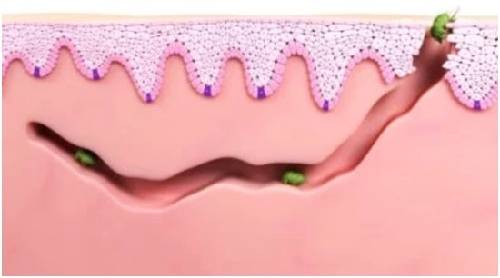
Scabies is an infestation of tiny mites called Sarcoptes scabiei in the outer layers of human skin. They dig tunnels or burrows underneath the skin's surface which causes the skin to become itchy. The mites belong to arachnid family, (the same family that includes spiders and ticks) and cannot be seen by the naked eye. They can be seen through a microscope only when they are fully grown.
The intense itching that results from scabies cause a red rash, that is thought to be caused by the immune system reacting to the mites, their eggs, saliva and droppings.
What causes scabies?
Scabies is caused by the female mites which dig under the top layer of skin to lay eggs. They die after about a month. Once the eggs hatch, new mites start growing and come to the skin surface. Underneath the skin, females mate with the males, following which the males die, and the females dig further under the skin to lay new eggs. This life cycle of the mites keep going on. It takes two to three weeks for the symptoms to show up after the mites have entered your system.
Who is at a risk of contracting scabies?
Those who are prone to scabies include:
- People with weak immune systems are at a greater risk of getting scabies such as HIV/AIDS patients, elderly people and children, people suffering from leukemia, lymphoma. People who have had any organ transplant are also at a greater risk.
- Since scabies is very contagious, when a single person in the household gets scabies there is every possibility that the other members of the household will get it too. Every member of the household needs to be treated as a precautionary measure when one person gets scabies.
- Sexual partners of the person infected with scabies are at a risk of getting infected with scabies.
- Any person who shares the personal belongings of an infected person, such as his bedding or clothing is at a risk of getting infected.
What are the symptoms of scabies?
The symptoms of scabies include:
- a pimple-like rash
- itching on the affected area
- open sores
- a crusted layer which is also known as Norwegian scabies. In this condition thousands of mites and eggs are harboured within skin crusts, causing severe skin symptoms.
In which parts of the body do the symptoms of scabies appear?
Scabies rash can appear on any part of the body. The most common sites are:
- wrists
- elbows
- armpits
- the skin between the fingers and toes and around the nails
- buttocks
- the belt line
- nipples
- genital area
- penis
Infants and young children may have scabies rash on their head, face, neck, palms, and soles.
How is scabies diagnosed?
Your family doctor or a general practitioner can easily diagnose scabies by looking at the skin condition and burrow marks of the Sarcoptes scabiei mite along the skin.
Since scabies spreads easily, other family members could also be infected easily, which makes the diagnosis easier for the doctor.
However, to rule out other skin conditions such as eczema, your doctor may ask you to undergo an ink test, in which ink is rubbed around an area of itchy skin, before being wiped off with an alcohol pad. After being wiped off, in cases of scabies, some of the ink remains, prominently showing the burrows dug up along the skin by the mites as a dark line. A skin sample may also be taken from you to test for eggs and mites.
If you have been diagnosed with scabies, the doctor may also ask you to go to a sexual health clinic to get yourself tested for sexually transmitted infections (STIs).
What are the complications of scabies?
The complications of scabies include:
- Norwegian scabies which is an extreme case of scabies, affecting people with a weak immune system, especially the one suffering from HIV or leukemia. In this condition patients develop a crusty layer or scaly sores all over the body underneath which there are thousands of mites and eggs.This condition is difficult to treat because even creams or lotions applied fail they are not able to seep in beneath the crusty layer.
- Breaking open of the skin due to vigorous scratching which can invite in a secondary bacterial infection, such as impetigo. Impetigo is caused most often by staph (staphylococci) bacteria or occasionally by strep (streptococci) bacteria. In impetigo reddening of skin occurs along with the formation of blisters and spores, which turn into a yellowish-brown colour at a later stage. These spores are filled with pus and are very painful. At an advanced stage, it is known to cause kidney inflammation as well.
What is the treatment of scabies?
If you have scabies the doctor will in all likelihood suggest the other family members also get treated as scabies infestation spreads easily. You will be prescribed oral medication as well as creams for topical application.
Patient Experiences




Did you know?
Women affected by scabies in India
Females affected the most by scabies in India are between the ages of 10-14 years old.
Women more affected
Prevalence of this disease seems to be higher among women than in men.
Related videos
Related articles
Syphilis is a very common Sexually Transmitted Disease (STD) which can spread through vaginal, anal, or oral sex. Know more about Syphilis, its causes, symptoms, treatment and other useful facts, links and videos on Health-Wiki | Practo
Nasal Polyps are referred to as the benign (non-cancerous) growth of the mucosa or lining tissues in the nose.
Malaria parasite is a mosquito borne disease. Read about symptoms, treatment, vaccine, test and home remedies for malaria. Find information, videos and facts for malaria on Health-Wiki | Practo

