
Contents
In this article we will look at:
- What is HIV positive?
- How does one get HIV?
- Who is prone to HIV?
- What are the causes of HIV?
- What are the symptoms of HIV?
- How is HIV diagnosed?
- What are the complications of HIV?
- Because I have HIV, will I eventually get AIDS?
- What can I do to stay healthy and avoid getting other infections
- How can I prevent passing HIV to others?
- Is there any reason to tell my employer and those I work with that I have HIV?
- What is the treatment of HIV?
You can click on any of the links above to navigate to the section of your interest.
What is HIV positive?
HIV stands for Human Immunodeficiency Virus. HIV positive means being infected with the HIV virus. Being infected with the HIV virus does not mean the person hasAIDS. People infected with HIV can be treated with HIV medicines. HIV medicines do not cure HIV but can help people infected with the virus to live longer, and healthier lives. Treatment with HIV medicines can prevent HIV from advancing to AIDS. AIDS is the final stage of HIV infection. AIDS modifies and corrupts the immune system, making people susceptible to infections and diseases. The susceptibility worsens as the syndrome progresses.
How does one get HIV?
A person can get HIV from an infected person through direct contact with bodily fluids such as:
- blood (including menstrual blood)
- semen / cum / precum / ejaculate
- vaginal secretions
- breast milk
The highest concentration of the virus is found in blood, followed by semen, followed by vaginal fluids, and then by breast milk.
HIV gets transmitted through:
- any form of sexual contact that involves semen, pre-cum, vaginal fluids or blood.
- contact with infected blood, especially through sharing infected injections, or through blood transfusions.
- mother to baby during or before birth or while breastfeeding the baby, through breast milk.
The HIV virus basically attacks your immune system and impairs its functions. Once the immune system is seriously damaged, your body loses its ability to fight certain infections and cancers.
The count of CD4 cells in a human body shows the immunity level of the person. A person with a healthy immune system has CD4 counts between 500 and 1,600 cells per cubic millimetre. When the number of CD4 cells fall below 200 cells per cubic millimetre of blood, then the HIV infection has advanced to the final stage of AIDS.
Once a person has been diagnosed with AIDS, she or he is always considered to be an AIDS patient, even if that person's CD4 count goes up again, or they recover from the disease that defined their AIDS diagnosis.
AIDS thus occurs when the immune system is irreparably damaged and you become vulnerable to what is known as opportunistic infections. Opportunistic infections are infections caused by pathogens (bacteria, viruses, fungi, or protozoa) and occur more often in people with weakened immune systems.
Though an HIV positive diagnosis can be very scary, there are many HIV positive people who are living healthy, happy lives by taking immediate treatment and managing their condition. Possible health effects of HIV can be easily prevented and managed with the correct treatment.
Who is prone to HIV?
Anyone of any age, race, sex or sexual orientation can be infected, but you're at greatest risk of HIV if you:
- have unprotected sex without using a condom
- have anal sex
- have multiple sexual partners.
- suffer from sexually transmitted infection which may cause sores in your genital area through which the HIV virus may enter your body.
- share needles and syringes for intravenous drugs
- an uncircumcised man
What are the causes of HIV?
The causes of HIV include:
- having unprotected sex with an HIV infected partner
- having oral sex (though the risk is low)
- sharing drug needles with someone who is infected with HIV
- the virus passing on from an expectant mother to her baby, during or before birth or while breastfeeding the baby, through breast milk.
- blood transfusion of infected blood
What are the symptoms of HIV? How is HIV diagnosed?
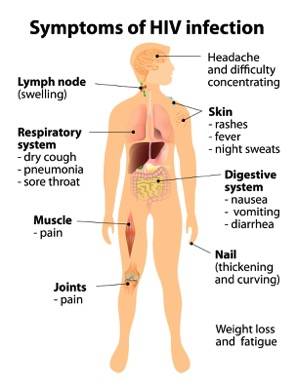
The most common HIV symptoms in men and women include:
- fever
- fatigue
- lack of energy
- skin rash
- muscle aches and joint pains
- headache
- sore throat
- weight loss (anorexia)
- nausea
- vomiting
- oral ulcers
- genital or anal ulcers
- weight loss
- night sweats
- persistent cough
- enlarged lymph nodes in the neck, armpits, and groin
- persistent diarrhea
Diagnosis
To diagnose HIV, the doctor will need:
- a confirmed, positive test for HIV, i.e. results showing HIV positive.
- evidence of an AIDS-defining condition or severely depleted CD4 cells.
Testing for HIV involves:
- a screening test
- a confirmatory test
For the screening test, either blood is obtained from a finger or a vein, or a urine sample or oral swab is taken. The results can be obtained on the same day or may take a few days.
If the result of the screening test is positive, the results are again confirmed by a special test called a Western blot or indirect immunofluorescence assay test. The confirmatory test is necessary because the screening test is not considered to be very accurate.
The first step is usually a screening test that looks for antibodies against the HIV. Specimens for testing come from blood obtained from a vein or a finger stick, an oral swab, or a urine sample. Results can come back in minutes (rapid tests) or can take several days, depending on the method that is used. If the screening HIV test is positive, the results are confirmed by a special test called a Western blot or indirect immunofluorescence assay test.
A Western blot detects antibodies to specific components of the virus. The confirmatory test is necessary because the screening test is less accurate and occasionally will be positive in those who do not have HIV.
If the confirmatory test results come back as positive, the person has a 99% likelihood of being infected with HIV.
Another way to diagnose HIV infection is to do a special test to detect viral particles in the blood. These tests detect RNA, DNA, or viral antigens. However, these tests are more commonly used for guiding treatment rather than for diagnosis.
What are the complications of HIV?
The complications of HIV infection include:
- Tuberculosis
- Cytomegalovirus
- Candidiasis
- Cryptococcal meningitis
- Toxoplasmosis
- Cryptosporidiosis
- Wasting syndrome
- Neurological complications
- Kidney diseases
- Memory impairment
Some cancers which are common among AIDS ( the advanced stage of HIV) patients are:
- Kaposi's sarcoma
- Lymphomas
- Cervical cancer in women
Because I have HIV, will I eventually get AIDS?
Though it cannot be said with surety for how long the average person who is HIV positive can live things are changing due to advances in medical science. A person even with full-blown AIDS can live for many years.
Majority of the people who are HIV positive will develop AIDS during their life, within a span of 10 years after contracting the virus or more. With early intervention and treatment
These are some of the variables that can determine how long a person who is HIV positive can live:
- People who lead a healthy lifestyle, i.e., exercise, take a healthy diet tend to live longer. Whereas, people living a sedentary lifestyle or who are involved with substance abuse have a shorter lifespan.
- People with drug-resistant strains of HIV may not have a long lifespan, since drugs may not be effective. But if a person is responding well to the medications, there is a strong possibility of them living a longer life.
- An emotionally healthy person will live longer. A positive frame of mind goes a long way in maintaining a healthy body and of course a sound mind.
- The genetic makeup of a person can sometimes slow down the progression of the disease.
- A lot also depends on the virulence of the particular strain of HIV. Some strains may not cause any significant illness.
What can I do to stay healthy and avoid getting other infections?
If you are diagnosed as HIV positive, a lot depends now on how you live your day to day life. If you manage your health with care you can live a healthy life for many years. A few things you can follow are:
- Go for treatment immediately once you are diagnosed. Starting antiretroviral treatment early is vital to maintaining a healthy and strong immune system.
- Eat healthy. Take plenty of fruits and vegetables. It is important to have a healthy intake of fibre, vitamins and minerals, and proteins. You can add lean meat, fish, eggs and beans, milk, yoghurt and cheese, and small amounts of fats and sugars to your diet.
- Exercising can help you to build your muscles and keep your bones strong. People with HIV tend to lose weight and develop weakened immune systems. A healthy diet coupled with daily exercise can increase your stamina and make you feel fitter. Some forms of exercise you can do are cardio or aerobics exercise, resistance training such as lifting weights, flexibility training such as yoga or any other forms of stretching exercises.
- Maintain a positive frame of mind. Do all the things you love the most to do, surround yourself with people who love and care for you. Your mental and emotional health goes a long way in having a sound physical body.
How can I prevent passing HIV to others?
A few precautions that you can take to protect yourself from HIV infection are:
- Reduce your number of sexual partners.
- Get your partners tested for HIV
- Have safe sex by using a condom
- Talk to your doctor about pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) which reduces the risk of getting HIV from sex by more than 90%. PrEP is an HIV prevention option for people who don’t have HIV but who are at high risk of becoming infected with HIV
- Do not use any form of drugs which you need to inject. Even if you do make sure you use only sterile drug injection equipment
Is there any reason to tell my employer and those I work with that I have HIV?
If your job is such that there are occupational restrictions for people living with HIV then you need to disclose the fact that you have HIV. Else you do not have to tell your employer about it. Moreover, it is against the law for employers to ask you any questions about your health before they offer you a job. If in case you are asked to disclose your HIV status after you have been offered a job, think carefully about how you respond, for failing to disclose might result in termination of your job. At the end of the day, the decision is yours. After a certain period of time, you may feel comfortable disclosing your HIV positive status.
What is the treatment of HIV?
Medical Treatment
There's no cure for HIV/AIDS, but a variety of drugs may be prescribed by your doctor to control the virus. The drugs are used in combination.
A few health issues that are a part of the natural ageing process, occurs earlier if you suffer from AIDS and may be more difficult to manage.
Medications may be prescribed for these conditions. However, some medications such as those for cardiovascular, metabolic and bone conditions, may not interact well with anti-HIV medications. You will need to discuss your conditions in detail with your doctor so that he/she can make sure your medicines do not react with each other.
You will be monitored every two to three months especially for your CD4 counts and viral load.
HIV treatment should reduce your viral load to the point that it's undetectable. Though, this does not mean you are free of HIV or that you will not transmit it to others.
Staying Healthy with AIDS
With a few precautions, you can lead a normal life even if you suffer from AIDS.
- Ask your doctor about vaccination so that you can get vaccinated if you have AIDS.
- Use condoms while having sex with your partner to avoid transmitting the disease and avoiding exposure to sexually transmitted infections.
- Avoid illicit drug use and needle sharing.
- Religiously take the medicines prescribed by your doctor to avoid any kind of AIDS-related complications.
- Take extra precautions when working or visiting hospitals or any other health care facilities so that you do not contract any infection.
- Avoid raw or undercooked products and unpasteurized dairy products.
- Wash your hands frequently when preparing foods.
- Drink filtered water.
- Join an HIV support group in your area. Support groups can immensely help boost your morale, keep you positively motivated and help you lead a healthy lifestyle.
Patient Experiences


Questions answered by trusted doctors
Can i take HIV test voluntarily without consulting doctor?
What HIV test need to be done after one year of possible exposure.


every disease and every test have different window period
hiv 1 pro viral dna QUALITATIVE test has window period of 17 days that means you have to do this test only after 17 days to get accurate result
HIV DUO has 3 month window period
RAPID HIV ELISA AND OTHER CARD TEST HAS 6 month window period
same way HBsAg, HCV and VDRL has window period of 3 month so you have to do it after 3 month of exposure.

17th Day of Exposure - HIV DNA Qualitative
43rd Day of Exposure - Westernblot
91st Day of Exlosure - Elisae Test

every disease and every test have different window period
hiv 1 pro viral dna QUALITATIVE test has window period of 17 days that means you have to do this test only after 17 days to get accurate result
HIV DUO has 3 month window period
RAPID HIV ELISA AND OTHER CARD TEST HAS 6 month window period
same way HBsAg, HCV and VDRL has window period of 3 month so you have to do it after 3 month of exposure.

Did you know?
2.1 million HIV Positive People In India
According to 2016 census there are approximately 2.1 million people in India who are HIV positive.
Heterosexual sex the main cause
The HIV epidemic in India is driven by heterosexual sex, which accounted for 87% of new infections in 2015.
Third largest HIV epidemic in the world
India has the third largest HIV epidemic in the world. In 2015, HIV prevalence in India was an estimated 0.26%.
Highest Concentration of HIV positive patients in India
The five states in India with the highest HIV prevalence (Manipur, Mizoram, Nagaland, Andhra Pradesh and Karnataka) are in the south or east of the country.
Related videos
Related articles
A wart is a small growth which is flesh-colored, tan, pink, or white and feels like a grainy bump on the skin. Know more about Warts Infection, its causes, symptoms, treatment and other useful facts, links and videos on Health-Wiki | Practo
When, in any part of the human body, there is loss of muscle function, it is called paralysis. This condition happens when something goes gravely wrong between the manner in which messages are passed by the brain and the muscles.
A sexually transmitted disease (STD) genital herpes is caused by a herpes simplex virus (HSV). Know more about Genital Herpes, its causes, symptoms, treatment and other useful facts, links and videos on Health-Wiki | Practo



