Contents
In this article we will look at:
- What is forceps delivery?
- When is forceps delivery performed?
- How is forceps delivery performed?
- What are the guidelines to be followed after a forceps delivery procedure?
- What are the guidelines to be followed after a forceps delivery procedure?
- When is a forceps delivery not advisable?
- What are the benefits of forceps delivery?
- What are the risks of forceps delivery?
- What to expect during the postpartum recovery period after a forceps delivery?
- More OB/GYN Related Topics
- References
You can click on any of the links above to navigate to the section of your interest.
What is forceps delivery?
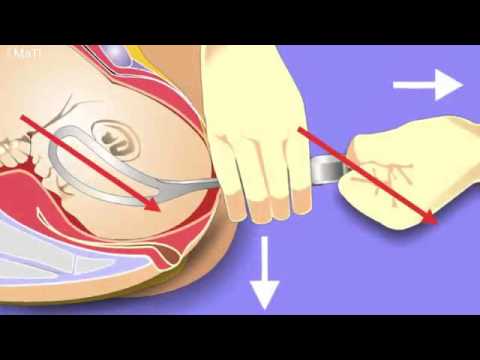
A forceps delivery is a form of assisted vaginal delivery which may sometimes be needed in the course of vaginal childbirth. Forceps is an instrument consisting of 2 metal ladle-like devices, (shaped like a pair of large spoons or salad tongs with a curve to snugly fit around the baby’s head), which are maneuvered to cradle and grasp the baby’s head and help guide the baby out of the birth canal.
Forceps are used to assist the delivery of a baby as an alternative to the vacuum extraction method.
When is forceps delivery performed?
Forceps assisted vaginal delivery is done during the second stage of normal vaginal delivery:
- when the mother is pushing but the labour has stalled
- if immediate delivery is required due to foetal distress (indicated by a change in the baby’s heartbeat suggesting that the baby’s health is at risk)
- if the mother suffers from certain health conditions due to which she cannot push for long periods such as aortic valve stenosis, (narrowing of the heart's aortic valve) blood pressure, aneurysm, glaucoma (if these health conditions are serious the doctor may recommend a caesarean procedure)
- if the baby is facing up (occiput posterior position) rather than down (occiput anterior position
How is forceps delivery performed?
Forceps delivery is done during the second stage of normal vaginal delivery. During this procedure:
- The doctor gently inserts two or more fingers inside your vagina and beside your baby's head.
- The doctor then gently slides one part of the tong between the fingers and the baby's head, followed by positioning of the other half of the tong on the other side of the baby's head.
- Both parts of the tong are then locked together to safely secure the baby’s head in between them.
- If the baby is facing upwards, in between the mother’s contractions, the doctor uses the forceps to gently shift the position of the baby’s head
- As the labour progresses the doctor may remove the forceps before the widest part of the baby’s head goes through the birth canal or he/she may retain the hold of the forceps.
- When the mother experiences the next contraction, the doctor gently guides the baby through the birth canal using the forceps.
Please Note: If after using the forceps the doctor is not able to move the baby after three pulls or the baby is not delivered within 20 minutes the doctor will most likely suggest an emergency C-Section. Alternatively, the doctor may also opt for vacuum extraction.
What are the guidelines to be followed after a forceps delivery procedure?
While using the forceps to assist in the delivery of the baby If the doctor had made an incision between the vagina and the anus during the delivery (episiotomy), or you had a vaginal tear there are a few things you can do to accelerate your healing:
- Ask the nurse to apply ice packs in the area of the wound right after birth. Once you come back home from the hospital continue using ice packs in the area.
- Use sitz baths a few times in a day once you get home from the hospital. This will provide relief from the pain.
- While urinating keep pouring warm water over the area, this will take away the sting of the urine.
- While passing stool do not put too much pressure. In fact, you can use a clean pad to firmly push against the wound during a bowel movement.
- After urinating or after a bowel movement spray some warm water in the area and pat dry using very soft towels or baby wipes. Do not use toilet paper or rub the area hard.
- While sitting down use a doughnut cushion or a pillow.
Immediately after the forceps-assisted delivery, your baby will be continuously monitored for any kind of complications related to forceps delivery.
What are the guidelines to be followed after a forceps delivery procedure?
While using the forceps to assist in the delivery of the baby If the doctor had made an incision between the vagina and the anus during the delivery (episiotomy), or you had a vaginal tear there are a few things you can do to accelerate your healing:
- Ask the nurse to apply ice packs in the area of the wound right after birth. Once you come back home from the hospital continue using ice packs in the area.
- Use sitz baths a few times in a day once you get home from the hospital. This will provide relief from the pain.
- While urinating keep pouring warm water over the area, this will take away the sting of the urine.
- While passing stool do not put too much pressure. In fact, you can use a clean pad to firmly push against the wound during a bowel movement.
- After urinating or after a bowel movement spray some warm water in the area and pat dry using very soft towels or baby wipes. Do not use toilet paper or rub the area hard.
- While sitting down use a doughnut cushion or a pillow
Immediately after the forceps-assisted delivery, your baby will be continuously monitored for any kind of complications related to forceps delivery.
When is a forceps delivery not advisable?
Forceps delivery is not advisable if:
- The mother’s pelvis is small and the baby cannot fit through the pelvis
- The mother is 34 weeks pregnant
- The position of the baby’s head is not clear
- The baby is known to have health conditions such as bleeding disorders (such as hemophilia), or conditions that may affect its bones
- The baby is emerging buttocks/feet first (breech position)
- The baby is emerging shoulder first
- The size of the baby is big
- The baby’s head has not moved past the midpoint of the birth canal
- Include plenty of fibrous foods in your diet to avoid constipation. Use stool softeners as well.
- Drink plenty of water.
- Doing Kegel exercises during this period with doctor’s advice will help. It will tone your pelvic muscles and bring strength back to them.
What are the benefits of forceps delivery?
Studies show that forceps-assisted deliveries are associated with less failure than vacuum extraction which may be of critical importance with fetal distress.
Women who have instrumental vaginal deliveries (vacuum assisted or forceps-assisted vaginal deliveries) typically have a shorter hospital stay and fewer readmissions than women who have caesarean sections.
What are the risks of forceps delivery?
Forceps delivery has its risks for both the mother and the baby.
The mother’s risks include:
- Vaginal tears during the delivery
- Bladder injuries
- Urethra injuries
Post the delivery the mother may experience:
- Fecal and/or urinary incontinence
- Perineum pain
- Difficulty while urinating
- Anemia
- Weakening of the muscles supporting the pelvic organs
The baby’s risks include:
- Bruising on the baby’s face due to the usage of forceps which disappears in a few days
- Nerve damage to the face caused by the pressure of the forceps
- Facial palsy
- Skull fracture
- Internal bleeding within the skull
- Temporary eye trauma for the baby due to the pressure of the forceps
- Seizures
What to expect during the postpartum recovery period after a forceps delivery?
After a vacuum assisted normal vaginal delivery you may face a few issues which will need some care such as:
- Vaginal discharge and bleeding: When bleeding, expect a heavy bright red flow for the first few days after the delivery as it happens during the monthly periods. It then slowly tapers off becoming pink or brown or yellow or white. You need to immediately call your doctor if you have fever or are bleeding too much and changing the sanitary pads every hour or you are passing big blood clots.
- Vaginal soreness: If you had a vaginal tear during delivery the wound may hurt for upto six weeks, though if the tearing was severe it could take more time than that to heal. While sitting down it can be painful, so you can use a pillow or a donut cushion that helps you to sit down with any pressure on the perineum.
You can place an ice pad between the sanitary napkin and the wound which will provide some relief from the pain.
Make sure you take your painkillers and stool softeners so that as recommended by your doctor.
- Pain while urinating or having bowel movements: As the tissue around your bladder and urethra may be swollen or bruised, you may find it painful to urinate. Doing Kegel exercises during this period with doctor’s advice will help. It will tone your pelvic muscles.
Further, you could also have constipation since you could be taking iron supplements which are prescribed by the doctor to get your blood count up. Make sure you take the stool softeners prescribed by the doctor. Also, drink plenty of water, 8-10 glasses per day to make up for the dehydration breastfeeding may cause, and add high-fiber foods to your regular diet.
If you notice very painful bowel movements you may also have haemorrhoids. To get relief from haemorrhoids you can soak the lower part of your body in a tub of warm water. You may also be prescribed some topical medication by the doctor to apply in the affected area.
- Contractions: Also known as after pains, contractions may occur for a few days immediately after delivery. These contractions are actually good in way as it means your uterus is shrinking back into size and the blood vessels are being compressed preventing excessive bleeding. Contractions can especially occur when you are nursing your baby.
- Hair loss: The rise in hormones during pregnancy keeps you from losing your hair. After childbirth, as the hormones return to normal levels it causes the hair to fall out and return to the normal hair fall and growth cycle. The normal hair loss that was delayed during pregnancy may fall out all at once after delivery.
- Mood changes: After childbirth it is normal for the new mother to undergo frequent mood changes such as irritation, frustration, anxiety etc . Many new moms also undergo what is known as postpartum depression. If the depression deepens the mother may need prompt therapeutic help in the form of psychological counselling.
More OB/GYN Related Topics
People interested in this topic also read:
- Childbirth & Delivery Methods
- Normal Vaginal Delivery
- Assisted Vaginal Delivery
- Caesarean Section
- Vaginal Birth After Caesarean
References
1. Sano Y, Hirai C, Takeda S, Makino S, Li X, Itakura A et al. Incidence and risk factors of severe lacerations during forceps delivery in a single teaching hospital where simulation training is held annually [Internet]. https://obgyn.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/. 2018 [cited 15 May 2018]. Available from: https://obgyn.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1111/jog.13558
2. Johanson R, Menon B. Vacuum extraction versus forceps for assisted vaginal delivery [Internet]. http://europepmc.org/. 2000 [cited 15 May 2018]. Available from: http://europepmc.org/abstract/med/10796182
3. Patel R, Murphy D. Forceps delivery in modern obstetric practice [Internet]. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC420176/. 2004 [cited 15 May 2018]. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC420176/

Did you know?
Pregnant women and nesting instinct
Very often pregnant women experience the need to organize, decorate, clean and ready the house in anticipation of the arrival of the baby. This is a ‘nesting instinct’ and is experienced by most of the pregnant women, though not all.
Pregnant women can experience lack of focus
Pregnant women due to the change of hormones during the first trimester may suffer from morning sickness and feel fatigued, and exhausted. This causes them to become forgetful, hazy, and lack focus.
A pregnant mother's food preferences influences the child's taste buds
What are your food preferences? Do you crave ice cream, fish, dairy products, or sweet foods? Chances are your baby will grow up with those being his/her favourite foods.
Related videos
Related articles
Rhinoplasty is known as nose job. It is a plastic surgery which helps in reconstructing and correcting the shape of the nose. Reconstructive surgery and Cosmetic surgery are the two types. Nose job helps in improving the appearance of the nose.
Attempting a vaginal birth after caesarean (VBAC), i.e. during the second pregnancy, is known as a Trial of Labor After Cesarean (TOLAC). Approximately 90% of the women who have undergone cesarean deliveries are possible candidates for VBAC.
Now with advancement in science and technology, modern medical practices have a number of options which have made childbirth a much safer experience over the past century for both the mother and the baby.