
Contents
In this article we will look at:
- How does arthritis occur?
- Who is prone to arthritis?
- Symptoms of arthritis
- Diagnosis of arthritis
- Complications of arthritis
- Treatment for arthritis
You can click on any of the links above to navigate to the section of your interest.
What is Acute Coronary Syndrome?
Acute Coronary Syndrome (ACS) is an umbrella term used to refer to a group of conditions, including myocardial infarction (heart attack) and unstable angina, which arise when the blood supply to the heart muscle is suddenly blocked.
How does Acute Coronary Syndrome occur?

The heart is primarily made up of the cardiac muscle.
The coronary arteries are responsible for supplying oxygen-rich blood to all the parts of the heart muscle.
The heart then contracts rhythmically, to pump blood into the different blood vessels, which carry it to different parts of the body.
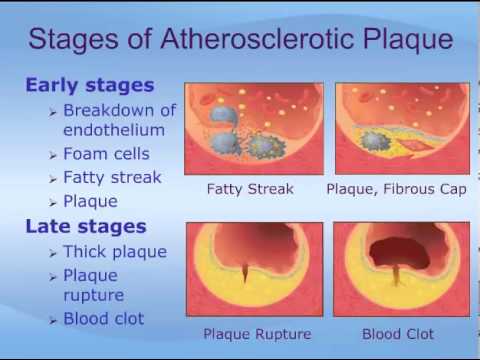
If any of the coronary arteries become narrow or blocked, due to cholesterol build-up and fatty deposits (a condition also known as atherosclerosis), the blood supply to that part of the heart gets affected. That particular part of the heart does not receive enough oxygen, and the tissue therein is at a risk of dying, unless the blockage is quickly removed. If left untreated, it can lead to a heart attack or unstable angina.
- A heart attack or myocardial infarction is caused when the blood flow to the heart, from the coronary arteries, completely stops due to a blockage. (The word infarction means death of some tissue due to a blocked blood vessel.)
- Unstable angina occurs when the blood flow to the heart slows down due to narrow arteries caused by cholesterol and fatty deposits or even blood clots.
There is also a condition known as stable angina, which is caused by sudden exertion, for example, after some rigorous exercise. This condition normally lasts from 1 to 5 minutes and is not considered very serious. It normalizes after some rest.
Doctors do not use the term Acute Coronary Syndrome while interacting with an affected patient. They usually use the term amongst themselves or in medical literature.
Who is prone to Acute Coronary Syndrome?
You are prone to ACS if you:
- have a high cholesterol level
- have high blood pressure/hypertension
- have a family history of heart disease
- are obese
- suffer from diabetes
- lead a sedentary lifestyle
- smoke excessively
Tobacco consumption is a major concern, with almost 40% of the ACS patients in India being chain-smokers. 38% of the ACS patients suffer from hypertension, while 30% of them also suffer from diabetes.
What are the symptoms of Acute Coronary Syndrome? How is Acute Coronary Syndrome diagnosed?
The ACS patients almost always complain of symptoms such as:
- severe chest pain, which gets worse with emotional stress or vigorous physical activity ( the pain can last from 15 mins to several hours)
- sweating
- breathlessness
- palpitation
A few patients also complain of giddiness, vomiting and abdominal pain.
Diagnosis
ACS is diagnosed with the help of an electrocardiogram, which reveals whether you suddenly suffered from a heart attack or whether you have angina. The electrocardiogram tests the heart’s electrical activity and measures the impulses. These impulses are recorded in the form of a graph on paper. The doctor checks the graph to see whether the heart is getting enough blood from the coronary arteries.
What are the complications of Acute Coronary Syndrome?
The complications of ACS depend upon the location of the blockage in the coronary artery, the amount of time it is blocked, and the size of the blockage. Depending on these factors various complications may arise.
• Pump Failure
When the blood flow to the heart gets affected it may lead to a heart attack. In a heart attack parts of the heart muscle, which do not receive oxygen, withers and dies which is then replaced by scar tissue. The scar tissue cannot contract and pump blood. On the contrary, the scar tissue may swell out or expand, when the rest of the heart muscle contracts to pump the blood, putting more pressure on the active parts of the heart to pump blood. Less blood may get pumped as a result, leading to less oxygen circulation in the body.
This may result in low blood pressure, heart failure and death.
• Cardiac Arrhythmias
Also called irregular heartbeat, cardiac arrhythmias is a condition where the heartbeat is irregular. It is either too fast or too slow. This can occur due to many reasons.
- An impaired heart might enlarge itself to make up for the decreasing pumping ability. The enlarged heart then beats more forcefully to pump blood, which affects the natural rhythm of the heart.
- Following a heart attack, the electrical impulses of the heart get affected which may cause the irregular heartbeats.
- Some parts of the heart which experience less blood flow, may not be dead but just be irritable. These irritable parts interfere with the natural rhythm of the heart. This condition is also known as ventricular fibrillation or ventricular tachycardia.
- An impaired heart might enlarge itself to make up for the decreasing pumping ability. The enlarged heart then beats more forcefully to pump blood, which affects the natural rhythm of the heart.
At times, cardiac arrhythmias can lead to heart failure or cardiac arrest.
• Mechanical Complications
The mechanical complications after a heart attack or death of some tissue in the heart include:
- a malfunctioning mitral valve, which can lead the blood to be pumped backwards, thus not supplying enough oxygen-filled blood to the body.
- ventricular wall rupture, which stops the blood supply to the body.
- left ventricular aneurysm, which is the swelling of a weak area in the wall of the left ventricle, the main pumping chamber of the heart. The swelling may block the passage leading to less blood flow to the body.
- a malfunctioning mitral valve, which can lead the blood to be pumped backwards, thus not supplying enough oxygen-filled blood to the body.
• Pericarditis
Pericardium is a tissue shaped like a two-layered thin sac which holds the heart in place, allowing it to perform its functions efficiently. The two layers have a small amount of pericardial fluid between them which keeps them from rubbing against each other. When pericarditis occurs the pericardium or the thin sac becomes inflamed and rubs against the heart. This causes chest pain and produces a rasping sound which is rhythmic that can be heard through a doctor’s stethoscope for around 2 days following a heart attack.
• Blood Clots
After a heart attack, blood clots form in the hearts of some people over the dead areas of the heart muscle. These blood clots can travel through the bloodstream and block passages impeding the blood supply to the rest of the body.
Other effects of ACS especially after a heart attack are shock, persistent depression and nervousness. A supportive family, breaking free from stress, and leading a healthy lifestyle goes a long way in managing and at times overcoming Acute Coronary Syndrome.
What is the treatment for Acute Coronary Syndrome?
Exercise
Following a regular regimen of exercise for just half an hour can be extremely beneficial for your heart health. Exercising strengthens and tones your muscles, which includes your heart, which is actually made of a muscle. It will keep your heart fit, helping it to pump blood and distribute it efficiently throughout your body.
It is advisable to consult with your cardiologist before starting an exercise regimen.
Medical Treatments
If only medicines do not suffice to restore normal blood flow through your arteries the doctor may suggest the following procedures:
- Angioplasty: In this procedure, the doctor inserts a thin tube called catheter into your blocked, or narrow plaque-ridden artery. Then he inserts a wire with an attached deflated balloon through the catheter, into the blocked area. Once inserted, the balloon is inflated which forces open the blocked area as the plaque is pushed against the walls of the artery.
- Coronary Intravascular Stent Placement: After the angioplasty procedure, a stent may be placed in the blocked area of the artery by the doctor, so that the area remains open and blood can flow through with ease. The stent is like a wire mesh tube, made of metal, which keeps the artery open at all times. Stents may be placed in multiple locations depending on the number of blocked arteries. The stents remain for life in the arteries.
- Coronary Artery Bypass Graft: Not all blocks in the arteries can be treated with angioplasty. If you have multiple blocks or have blocks which are inconveniently placed, the doctor may advise coronary artery bypass grafting. This is a process in which the doctor will take a healthy artery, or vein, from any part of the body, including, legs, chest, or the wrist, and graft or connect, one end of it of the vein above the blocked artery, and the other end below the block. This way, the blood flows through the newly grafted artery and goes around, or bypasses the blocked part of the coronary artery, to reach the heart.
Questions answered by trusted doctors

Did you know?
India as the highest number of ACS cases
India carries the highest burden of ACS in the world. It is seen that Indian patients with ACS have a higher rate of major ( as opposed to minor ) heart attacks, often proving fatal.
Men suffer from ACS more than women
It has been generally observed that men in India suffer from ACS four fold more than women. This is of course taking into consideration the fact that women approach the doctors much later than men, since they seem to have more tolerance of pain than men.
Age range
The age range of the patients in India with ACS is 31 to 81 years old with the average age being 55 years. The risk of ACS increases with age.
Related videos
Related articles
Pancreatitis which occurs in the pancreas, is caused due to pathological inflammation in the pancreas. The pancreas help in digestion of the food by secreting digestive enzymes.
Dialysis is a procedure in which the blood is filtered mechanically without the help of the kidneys. If the kidneys are not functioning properly then Dialysis will take over the function of the failed kidneys.
CHF stands for Congestive Heart Failure in medical terminology.


.AND NO obus clot is it necessary of CAG.
Lv dysfunction. Please suggest