
Contents
In this article we will look at:
- What is endometriosis?
- How does endometriosis occur?
- Who is prone to endometriosis?
- What are the causes of endometriosis?
- What are the symptoms of endometriosis?
- What is bladder endometriosis? What are the symptoms of bladder endometriosis?
- What is bowel endometriosis? What are the symptoms of bowel endometriosis?
- How is endometriosis diagnosed?
- What are the complications of endometriosis?
- What is the treatment for endometriosis?
You can click on any of the links above to navigate to the section of your interest.
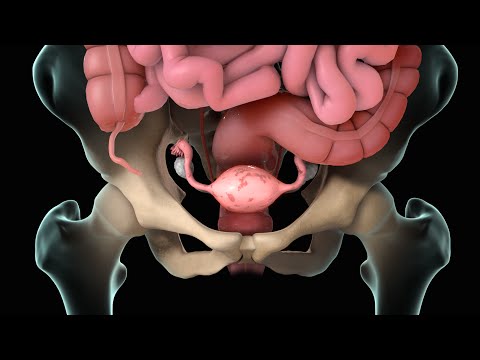
What is endometriosis?
Endometriosis is a painful gynecological condition, which occurs in women when the tissue that makes up the uterus lining develops elsewhere in the body.
Women with endometriosis often suffer from infertility, lower abdominal pain, pain during menstruation, or pain during sexual intercourse. Some women with endometriosis, however, may not have any symptoms at all.
How does endometriosis occur?
Every month hormonal changes in women cause the lining of the womb to thicken, to prepare itself for pregnancy. When the pregnancy does not occur, the cells break down and bleed out of the body naturally, which is the monthly menstruation cycle.
In endometriosis, the womb cells or the tissue that makes up the uterus lining grows in other parts of the body, such as the ovaries, fallopian tubes, the exterior of the uterus, the bowel, or other internal parts. Now, these cells too go through the same monthly cycle and break down during menstruation. But unlike the cells lining the womb, these cells have no outlet to leave the body once they break down. This can cause inflammation and scar tissue to form.
There are different types of endometriosis:
Peritoneal endometriosis: which occurs when cells which form the uterus lining stray into different parts of the body and accumulate till they become scar tissue.
Endometriosis of ovary: these start as coloured spots and form deposits which can go deeper into the ovary, where they eventually create cysts.
Adenomyosis: which occurs when the endometrial tissue grows into the muscle layer of the uterus damaging the uterine wall. It usually affects women over 30 who have had several births.
Rectovaginal septum endometriosis: affects ligaments between the uterus and pelvic bones causing adhesions.
Who is prone to endometriosis?
Some women are more prone to endometriosis than others. They include women who:
- have a family history of endometriosis
- are pregnant for the first time at an older age
- suffer from heavy bleeding during periods
- have periods which last longer than five days
- have their first period before 11 years of age
- regularly have less than 27 days between periods, or having shorter regular cycles
- have experienced sudden changes in the immune cells
- are underweight
- overindulging in alcohol
- have retrograde menstruation. Retrograde menstruation occurs in almost all menstruating women (up to 90 %) and therefore is considered a natural process. Retrograde menstruation occurs when, during menstruation, the blood flows out of the vagina, but also backwards along the fallopian tubes into the pelvis. In majority of the women the blood, which contains endometrial cells is absorbed or broken down and causes no symptoms. However, problems arise when larger volumes of menstrual fluid reach the pelvic cavity. This is when endometriosis occurs.
What are the causes of endometriosis?
The causes endometriosis are not known, however, there can be many risk factors which can vary from person to person such as:
- a family history of endometriosis
- being pregnant for the first time at an older age
- suffering from heavy bleeding during periods
- having periods which last longer than five days
- having their first period before 11 years of age
- having less than 27 days between periods
- sudden changes in the immune cells
- being underweight
- overindulging in alcohol
- retrograde menstruation
What are the symptoms of endometriosis?
Endometriosis symptoms include:
- pelvic pain and discomfort
- painful, heavy and/ or irregular periods
- pain during or after sex
- painful bowel movements
- stomach bloating
- back pain
- leg pain
- depression
- constipation
- fatigue
- fertility issues
- pain during urination
- diarrhea
Since some of the symptoms of endometriosis are similar to Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS), acute appendicitis, interstitial cystitis, or celiac disease, there are possibilities of misdiagnosis. In fact what is commonly known as bladder and bowel endometriosis can get misdiagnosed easily to be irritable bowel syndrome or appendicitis.
What is bladder endometriosis? What are the symptoms of bladder endometriosis?
Bladder endometriosis occurs when endometrial-like cells grow on or through the walls of the bladder. Symptoms include:
- frequent urination
- pain on urination
- urinary urgency
- urinary retention
- bloody urine
What is bowel endometriosis? What are the symptoms of bowel endometriosis?
Bowel endometriosis occurs when endometriosis affects the ileum, (which is part of the small intestine). The symptoms include:
- pain on the right side of the abdomen that mimics acute appendicitis
- bowel obstructions
- constipation which can last for weeks
- rectal pain and bleeding
How is endometriosis diagnosed?
Endometriosis can be treated by a gynecologist. The doctor will first ask you for your medical history and then ask you to describe your symptoms. He/ she will perform a pelvic exam manually for abnormalities such as cysts. The doctor will ask you to undergo tests such as :
- Ultrasound
- Laparoscopy
- For bladder endometriosis, the doctor may suggest a biopsy, where a portion of the endometrial implant is sampled from inside the bladder. This will rule out other causes of bladder symptoms, such as interstitial cystitis or rarely, bladder cancer.
- For bowel endometriosis, the doctor may suggest laparoscopy and proctoscopy (a procedure in which a camera is placed in the rectum) or a CT scan of your abdomen. If you suffer from rectal bleeding your consulting gynecologist may also suggest you be evaluated by a gastrointestinal specialist to rule out the possibility of colon cancer.
What are the complications of endometriosis?
The complications of endometriosis if treatment is delayed, include:
- fertility issues
- adhesions – 'sticky' areas of endometriosis tissue that can join organs together
- ovarian cysts that can sometimes become very large and painful
- bowel obstructions
- constipation which can last for weeks
- rectal pain and bleeding
- frequent urination
- pain on urination
- urinary urgency
- urinary retention
What is the treatment for endometriosis?
Medical Treatment for Endometriosis
Currently, there is no cure for endometriosis. The aim of the treatment for endometriosis is to reduce the severity of the symptoms and the hormones that contribute to the issue.
Based on the severity of your condition the doctor may prescribe medicines which include painkillers, anti-depressants, contraceptive pills. For more severe cases the doctor may suggest laparoscopy, bowel surgery, hysterectomy, or oophorectomy.
Exercise
Endometriosis patients can experience noticeable relief from their symptoms when they include exercise in their daily routine. It is advisable to consult a doctor though before deciding on any form of exercise regimen to find out what exercises will be most suitable, based on the symptoms.
Exercises such as yoga, weight training, pilates, walking or jogging can not only boost up physical energy but also boost one up mentally.
Patient Experiences


Questions answered by trusted doctors


Did you know?
Women affected by endometriosis worldwide
Endometriosis is a common medical problem affecting about 89 million young women in the reproductive age group worldwide.
Complications due to endometriosis
Endometriosis is the main reason for stomach pain and inability to conceive in women between 25 to 30 years of age.
Endometriosis and infertility
About 30 and 40 % of women with endometriosis are infertile.
Related videos
Related articles
A female condom is a device used by women during sexual intercourse with a man as a shield against unwanted pregnancy. Know more about female condom, its uses and other useful facts, links and videos on Health-Wiki | Practo
Monthly periods, or menstruation or the menstrual cycle is body’s way of preparing for pregnancy each month in a woman. It is when the body sheds the lining of the uterus and the menstrual blood flows from the uterus through the cervix and the vagina and
This is a minimally invasive surgical procedure using a laparoscope to remove the uterus and/or fallopian tubes and ovaries through the vagina.



Warm baths and a heating pad can help relax pelvic muscles, reducing cramping and pain.
Take pain killers when its required