Contents
In this article we will look at:
- What is eczema?
- How does eczema occur?
- Who is prone to eczema?
- What are the causes of eczema?
- What are the symptoms of eczema?
- How is eczema diagnosed?
- What are the complications of eczema?
- What is the treatment for eczema?
You can click on any of the links above to navigate to the section of your interest.
What is eczema?
Eczema is the name for a group of conditions that cause the skin to become red, itchy and inflamed. The word 'eczema' comes from a Greek word that means 'to boil over,' which is in fact a good description considering that when one suffers from eczema, the skin flares up and becomes red, inflamed, itchy, and patchy.
This is a very common condition among babies and children. It can appear on any part of the body.
How does eczema occur?
Although the exact cause of eczema is unknown, it is thought to be an overactive response by the immune system of the body to an irritant. It is this response which causes the symptoms of eczema.
Eczema is common among people whose families have a history of allergies or asthma.
There are eight different types of eczema:
Atopic Dermatitis: Atopic refers to a personal and family tendency to develop eczema, asthma and/or hay fever.
Discoid: This is a chronic skin condition of sores with inflammation. These lesions have a scaling and crusty appearance.
Contact Dermatitis: is the most common type of work-related skin disease. It occurs when occurs when the skin develops an allergic reaction after being exposed to a foreign substance.
Adult Seborrheic: It is a common skin disease It's a common skin disease that looks similar to psoriasis that commonly affects adults. It tends to affect the scalp, face, torso and flexures.
Infantile Seborrhoeic: It is a condition that can affect infants and cause yellow, crusty, greasy scaling frequently on the scalp skin
Pompholyx: The key characteristic of pompholyx eczema is blistering that is restricted to the hands and feet.
Asteatotic Eczema: Asteatotic eczema almost always affects people over the age of 60. It is a form of eczema in which the skin becomes abnormally dry, itchy and cracked.
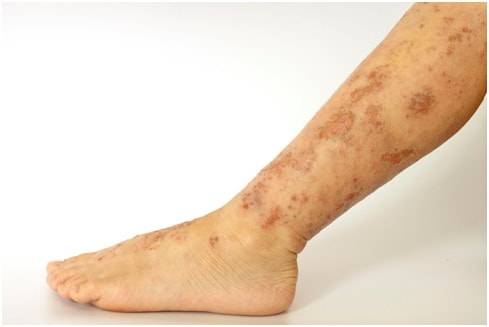
Varicose Eczema: Varicose eczema, also known as venous, gravitational or stasis eczema, is a long-term skin condition that affects the lower legs. In this condition skin discolouration and thickening occurs.
Atopic dermatitis seems to be the most common form of eczema, although it is possible to have more than one type of eczema at a time.
Who is prone to eczema?
Some people may be more prone to eczema than others. They include:
children who live in cold climates
people who live in urban areas, which are usually highly polluted
people who live in a climate that is dry all year-round
people who experience low humidity in the winter
people who are prone to allergies
What are the causes of eczema?
The causes of eczema can include:
Genetics or having family members who have had asthma, eczema or allergies such as hay fever.
Suffering from problems with the immune system.
Environmental factors such as exposure to toxic substances, high levels of pollution or extreme climate.
Certain defects in the skin that affect the functioning of the skin to act as a barrier against germs
What are the symptoms of eczema? How is eczema diagnosed?
The common eczema symptoms include:
dry and itchy skin
sensitive skin
redness and inflammation of the skin
irritation on the skin
rough and scaly or leathery patches of skin
crusting or oozing from the patches on the skin
swelling of the affected skin area
Diagnosis
There are no specific tests to determine eczema. The doctor who can be a paediatrician, a dermatologist, or your primary care provider can make a diagnosis of eczema by looking at your skin and by asking a few questions.
The doctor may suggest some allergy tests (especially if it is child), since many people suffering from eczema also have allergies.
What are the complications of eczema?
The complications of eczema include:
dry skin
erythroderma (exfoliative dermatitis), another type of inflammatory skin condition which can worsen the condition of eczema
people with eczema have a lower resistance to the herpes simplex virus, which is the virus that causes cold sores
itching, which may be severe, especially at night
red to brownish-grey patches, especially on the hands, feet, ankles, wrists, neck, chest, eyelids, elbows and knees. In infants, the patches may appear on the face and the scalp
sleep disturbances
small, raised bumps, which may leak fluid and crust over when scratched
thickened, cracked, scaly skin
attention deficit hyperactivity, which studies show is linked to eczema
raw, sensitive, swollen skin from scratching
eye problems such as conjunctivitis, keratoconus (cone-shaped eyeball), cataracts, and retinal detachment.
self-esteem issues
hay fever, or food allergies
What is the treatment for eczema?
The doctor based on your condition may prescribe oral medicines along with an ointment for topical application. He may also suggest some moisturizers for daily application on the affected areas.
Patient Experiences



Questions answered by trusted doctors



Did you know?
Eczema more common among the elderly
Eczema, benign skin tumors, and pigmentary disorders are more common in people aged 51 years and above, and fungal infection and acne are more common in adolescent age groups in India.
More common among women
Prevalence of eczema is higher among women than in men in India
Related videos
Related articles
The Inflammation of your bronchial tubes (bronchi) is known as bronchitis. Know more about Bronchitis, its causes, symptoms, treatment and other useful facts, links and videos on Health-Wiki | Practo
A viral infection, the human papillomavirus (HPV) gets transmitted from person to person through skin contact and can cause Sexually Transmitted Infections (STIs).
Dialysis is a procedure in which the blood is filtered mechanically without the help of the kidneys. If the kidneys are not functioning properly then Dialysis will take over the function of the failed kidneys.


