
Contents
In this article we will look at:
- What is COPD?
- How does COPD occur?
- What are the causes of COPD?
- Who is prone to COPD?
- What are the symptoms of COPD?
- How is COPD diagnosed?
- What are the complications of COPD?
- What is the treatment of COPD?
You can click on any of the links above to navigate to the section of your interest.
What is COPD?
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) is an umbrella term, used to describe a group of progressive lung diseases, including emphysema, chronic bronchitis, refractory (non-reversible) asthma, and some forms of bronchiectasis. Most people with COPD usually have both emphysema and chronic bronchitis.
COPD causes obstructed airflow from the lungs and results in symptoms such as shortness of breath, chronic cough, and wheezing.
Symptoms may be mild at first, beginning with coughing and shortness of breath. As the disease progresses, it can become increasingly difficult to breathe.
How does COPD occur?
COPD is mainly caused by cigarette smoking. The longer one smokes the greater the risk of contracting COPD. Regular inhaling of second-hand smoke can also cause COPD.
Prolonged exposure to air pollutants, dust, workplace fumes, biomass smoke such as wood smoke too are causes of COPD.
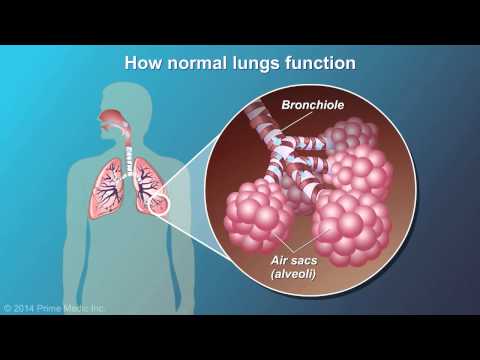
When we breathe in, oxygen-rich air goes down the windpipe and into small bronchial tubes or airways located in the lungs. These bronchial tubes branch off into numerous tinier tubes which are known as bronchioles. At the end of the bronchioles are some small, round air sacs called alveoli, which have tiny blood vessels known as capillaries. When the air enters the alveoli, oxygen travels through the capillaries and then into the bloodstream and carbon dioxide moves into the alveoli so we can breathe it out.
What smoking or air pollutants do is damage the walls between the air sacs so that they become weak over time, and their walls break open. This creates one large air sac, instead of the multiple tiny ones making it more difficult for the capillaries to absorb enough oxygen and for the body to expel the carbon dioxide. As a result, the affected person struggles to breathe.
What are the causes of COPD?
The causes of COPD include:
- smoking cigarettes
- exposure to fumes from burning fuel for cooking and heating in poorly ventilated homes
- prolonged exposure to air pollutants, dust, workplace fumes
- secondhand smoke
- Infectious diseases that destroy lung tissue in patients
Who is prone to COPD?
People who are prone to COPD include:
- those who smoke regularly
- those who are exposed to secondhand smoke from tobacco
- injection drug users
- those who have immune deficiency syndromes
- those who have connective tissue disorders
- those who suffer from genetic problems such as Salla disease
What are the symptoms of COPD? How is COPD diagnosed?
The early symptoms of COPD include
- shortness of breath, especially after exercising
- recurrent cough with mucus
- needing to clear your throat often, especially first thing in the morning
- fatigue
As lungs get more damages the symptoms become more severe:
- shortness of breath, after even mild exercise such as walking up a flight of stairs
- wheezing or a whistling or squeaky sound while breathing
- chest discomfort or tightness
- chronic cough, with or without mucus
- need to clear mucus from your lungs every day
- frequent colds, flu, or other respiratory infections
- lack of energy
In advanced stage the symptoms of COPD include:
- swelling of the feet, ankles, or legs
- weight loss
Diagnosis
A general practitioner can diagnose COPD, however, if your condition is too severe he may refer you to a pulmonologist. The doctor will start the diagnosis by asking you about your habits such as smoking, your lifestyle, i.e., if you are exposed to secondhand smoke, air pollution, dust, and chemicals on a daily basis, and your past medical history. He may suggest you undergo some tests such as:
- Spirometry to test of how well your lungs work.
- Chest x-ray which can show emphysema, one of the main causes of COPD and also rule out other lung conditions or heart failure.
- Arterial blood gas test, which measures the oxygen level in your blood.
- CT scan of your lungs which can help detect emphysema and determine if you might benefit from surgery for COPD.
What are the complications of COPD?
The complications of COPD include:
- Arrhythmia
- Depression
- Coronary Artery Disease
- Pneumonia
- Heart failure
- Lung cancer
- Right-Sided Heart Failure
- Trouble sleeping
- Dementia
- Death
What is the treatment of COPD?
Medical Treatment for COPD
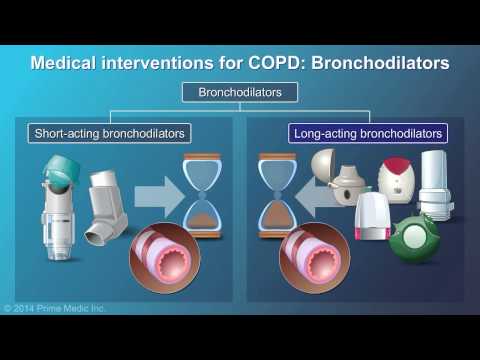
If smoking is the cause of COPD, the doctor will ask you to stop smoking immediately. He may then, based on the severity of your condition, prescribe bronchodilators which are to be taken with inhalers. Bronchodilators relax the muscles around your airways, antibiotics, inhaled steroids, and oral steroids. If your condition is very severe, the doctor may further suggest oxygen therapy and pulmonary rehabilitation program. For extreme cases, surgery may be required, which can include lung transplant.
Exercise
It may seem difficult to exercise as you have trouble breathing due to COPD, but exercising regularly can improve your overall strength and endurance and also strengthen your respiratory muscles. It is highly advisable to discuss with your doctor which exercises will be appropriate for you.
Exercises which are usually recommended for COPD patients include walking, cycling, Tai Chi. For people with mild COPD jogging, rowing, skating, water aerobics are some good forms of exercises.
Questions answered by trusted doctors

Did you know?
COPD, unrecognized epidemic in India
India is experiencing a continued increase in burden of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). With an estimated prevalence of >57.000.000 people suffering from obstructive airway diseases (OADs), by the end of 2016, India is in second place for harbouring the most number of morbidity and mortality cases from OADs, after China.
India ranks first in lung disease deaths
As many as 142.09 in every one lakh, died of one form of lung disease or the other in 2014-2015 giving India the dubious distinction of ranking first in lung disease deaths in the world.
Related videos
Related articles
Chickenpox is a highly contagious viral illness, characterised by an extremely itchy red rash. Find out about chickenpox vaccine, symptoms, virus. Get information, videos and facts about Chickenpox on Health-Wiki | Practo
Tuberculosis is a potentially dangerous bacterial disease, affecting the lungs and is caused by an organism called Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Know more about Tuberculosis, its causes, symptoms, treatment and other useful facts, on Health-Wiki | Practo
Gastritis is an inflammation and erosion of the stomach lining, due to bacterial infection, certain pain killers, drinking too much alcohol, very spicy food. Know more about Gastritis, its causes, symptoms, treatment videos on Health-Wiki | Practo.

What are the complications associated with a COPD patient undergoing surgery?
Hence it is just the question of how safley the job is done with out causing harmful effects .
So if u feel u can do it that way it is ok.
Also try to use some face mask like protective devices to reduce the dust exposure