
Contents
In this article we will look at:
- What is tonsillitis?
- What are the causes of tonsillitis?
- Who is prone to tonsillitis?
- What are the symptoms of tonsillitis?
- How is tonsillitis diagnosed?
- What are the complications of tonsillitis?
- What is the treatment for tonsillitis?
- In the Spotlight- Latest News on Tonsillitis
You can click on any of the links above to navigate to the section of your interest.
What is tonsillitis?
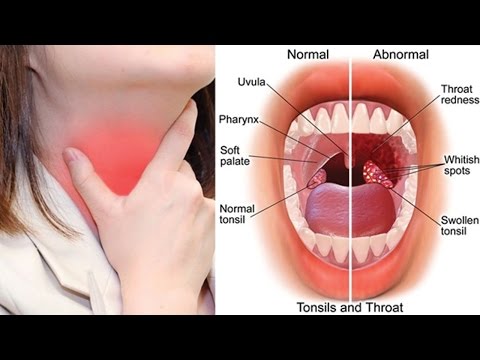
Tonsils apart from adenoids are the human body's first line of defense as part of the immune system. Tonsils are two lumps, similar to lymph nodes situated at the back of the throat.
They filter bacteria and viruses that enter the body through the mouth or nose, but they themselves can sometimes become infected. Tonsillitis is an infection of the tonsils caused by viruses and bacteria. When tonsillitis occurs the tonsils get inflamed and swell up causing nasal obstruction and/or breathing, swallowing, and sleep problems. Tonsillitis usually is contagious for about 7-10 days.
What are the causes of tonsillitis?
Tonsillitis is inflammation of the tonsils due to infection by viruses and bacteria. It is a very common childhood condition and can occur at any age. Tonsils produce white blood cells which combat viruses and bacteria that enter the body through the mouth. But if the immune system is weak, especially in children, overworked, and elderly people then the tonsils become vulnerable during the attack by the viruses and bacteria and get infected.
The most common cause of tonsillitis is viruses. The viruses cause infections such as the common cold and flu, and there is the EBV virus (part of the herpes family which spreads through bodily fluids, most commonly through kissing) that causes mononucleosis or mono also known as the kissing disease. Here are some of the common viruses that cause tonsillitis:
- Adenoviruses
- Influenza virus
- Epstein-Barr virus
- Parainfluenza viruses
- Enteroviruses
- Herpes simplex virus
The most common bacterium that causes tonsillitis is the one that causes strep throat especially in children, called Streptococcus pyogenes.
Who is prone to tonsillitis?
The people most prone to tonsillitis are:
- Children especially between the ages of 3 and 7 (viral tonsillitis)
- Children between 5 to 15 years (bacterial tonsillitis)
- Overworked people
- Elderly people
- People frequently exposed to crowded places
What are the symptoms of tonsillitis?
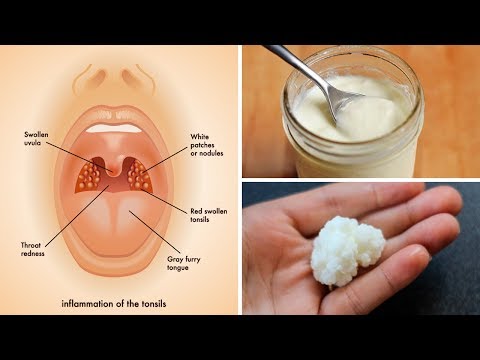
The symptoms of tonsillitis include:
- Throat pain
- Nasal congestion
- Runny nose
- Enlarged or swollen tonsils
- A whitish or yellowish coating on the tonsils
- Sore an itchy throat
- Difficulty in swallowing
- Raspy voice
- Bad breath
- Headache
- Fever
- Disturbed sleep
- Nausea
- Ear pain
- Jaw pain
- Vomiting
- Stomach pain
How is tonsillitis diagnosed?
A general physician asks for the medical history of the patient and then performs a physical examination. He checks the throat for swollen tonsils and also looks at the nose and ears. He listens to the breathing using a stethoscope. For severe cases, the doctor might ask a swab test to be done in which the doctor rubs a sterile swab over the back of the patient ’s throat to get a sample of secretions. This sample is then sent to the laboratory for testing. The swab test is especially done to determine if the cause of the infection is streptococcal bacteria.
What are the complications of tonsillitis?
Inflammation or swelling of the tonsils from frequent or ongoing (chronic) tonsillitis can cause complications such as:
- Difficulty in breathing
- Poor sleep
- Extreme pain while swallowing
- Extreme fatigue and weakness
- Drooling
- Middle ear infection (otitis media) causing ear pain
If you face any of the above complications you need to consult a doctor immediately.
Very rare complications of tonsillitis can occur if the underlying bacterial infection is not treated, or if the antibiotic treatment is incomplete. They include:
- Scarlet fever
- Rheumatic fever
- Glomerulonephritis or infection of the filters in the kidneys that causes vomiting and loss of appetite
What is the treatment for tonsillitis?
Treatment for tonsillitis depends largely on the cause. If the cause is a bacterial infection, antibiotics will be prescribed.
Viral infections do not show up on tests, however, if the bacterial tests come back as negative it can be safely assumed that it is a viral infection. If the cause is viral infection antibiotics will not help, and your immune system will fight off the infection on its own. In the meantime, you can follow the simple home remedies provided below, apart from complete bed rest, which can bring adequate relief.
In the Spotlight _ Latest News on Tonsilitis
Here are some latest news on tonsilitis:
Questions answered by trusted doctors

Did you know?
Tonsilitis affects children more
Tonsillitis most commonly affects children between preschool ages and the mid-teenage years. In children who are unable to describe how they are feeling the symptoms of tonsilitis include, difficulty swallowing, drooling, irritation, fussiness, fever, and refusing to eat.
Prevention is better than cure
The viruses or bacteria that cause tonsilitis are highly contagious, therefore advise your child to wash his/her hands thoroughly especially after a visit to the toilet and prior to eating, avoid eating shared food from the same plate, and sneeze into a tissue or a hanky.
Related videos
Related articles
Nipah Virus Symptoms, Treatment, Transmission and Outbreak. Know more about Nipah Virus, User stories, Doctor answered questions, Videos and Facts on Nipah Virus on Health-Wiki | Practo.
Swine flu disease spreads among pigs through direct and indirect contact, aerosols, and from infected pigs that do not experience symptoms. Know more about Swine Flu, its causes, symptoms, treatment and other facts, and videos on Health-Wiki | Practo
Dialysis is a procedure in which the blood is filtered mechanically without the help of the kidneys. If the kidneys are not functioning properly then Dialysis will take over the function of the failed kidneys.


IF YOU TAKE THERE AFTER NOPROBLEM WILLBE THEIR.
TABLET SIGMOFALM THREE TIMES OR TWO TIMES A DAY AFTER FOOD FOR THREE TO FIVE DAYS.
TABLET CEFADROXIL500 TWO TIMES A DAY AFTER FOOD.
PLENTY OF LUCK WARM WATER.
TOMATO SOUP, VEGETABLE SOUP SIP BY SIP.
LIGHT DIET.
O.K, BYE.