Contents
In this article we will look at:
- What is mumps?
- How does mumps occur?
- Who is prone to mumps?
- What are the symptoms of mumps?
- How is mumps diagnosed?
- What are the complications of mumps?
- What is the treatment for mumps?
You can click on any of the links above to navigate to the section of your interest.
What is mumps?
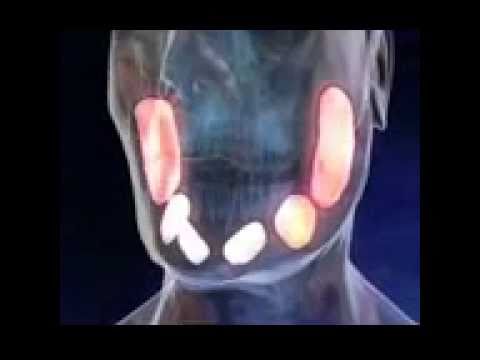
Mumps is a highly contagious disease, caused by the mumps virus, which affects the salivary glands or the parotid glands of a person. You can get infected with mumps via droplets of saliva from the mouth, mucus from the nose, or throat of an infected person, usually when the person sneezes, coughs, or talks.
The most noticeable feature of this disease is that the infected person develops a painful swollen ‘hamster-like face’, or ‘chipmunk cheeks’. This well-known symptom, however, is also the last one to present itself, after high fever, headache and general flu-like symptoms.
If you suspect that you have been exposed to the mumps virus contact your family physician or a general physician immediately.
It is also advisable to let your doctor know in advance that you are coming for consultation for suspected mumps so that the doctor can take adequate precautions against the spread of infection.
Please note, receiving a vaccine after getting exposed to the virus will not prevent the disease from occurring. However, if you did not get infected after the particular exposure, a vaccine may protect you against future infections of the mumps virus.
How does mumps occur?
The virus travels in the air through droplets of saliva and mucus when an infected person sneezes, coughs, or talks.
It can land on various surfaces, such as door handles, and cutlery and linger on for sometime. When an unsuspecting person touches these surfaces and then rubs his mouth or nose, he gets infected. The incubation period of the mumps virus is 7-18 days, and on an average is around 10 days after the exposure.
An infected person experiences the symptoms 2-3 weeks after the exposure.
However, not all people experience the symptoms of mumps. One out of three people suffering from mumps do not experience any symptoms at all. Mumps is a very common infection among children. This disease can be prevented through vaccination. There is a limitation however as people who :
have a compromised immune system,
are allergic to ingredients in the vaccine
are pregnant
cannot take the vaccine.
After suffering from mumps once, a person develops immunity to it. There are, however, rare cases of mumps occurring a second time in some people.
Who is prone to mumps?
Those who work in high-risk environments such as hospitals and schools are highly susceptible to the mumps virus and should be vaccinated against mumps.
Children below the age of six years, as well as adults who have not received the vaccination, are at a high risk of contracting mumps.
- People who have a compromised immune system are at a high risk of contracting mumps which can also lead to serious complications.
What are the symptoms of mumps? How is mumps diagnosed?
The symptoms of mumps usually appear between 12 and 25 days after a person has been exposed to the mumps virus. The symptoms include:
painful swollen and puffy cheeks
flu-like symptoms including sneezing, coughing, and high fever (103F)
weakness and tremendous fatigue
muscle and body pain
pain in the throat while swallowing and drinking
abdominal pain in adolescent girls due to swollen ovaries
pain in testicles among adolescent boys
dry mouth
loss of appetite
Diagnosis
A general physician can diagnose mumps from the symptoms alone, especially from the swollen cheeks. The doctor may ask you to undertake blood, saliva, or urine test to confirm that you suffer from mumps. In the most severe cases, the doctor may take a sample of the cerebrospinal fluid for testing.
What are the complications of mumps?
Several complications can occur with mumps, but as the infection passes away they vanish. The complications include:
swollen and painful testicles in boys also known as Orchitis
swelling of ovaries in females which can be painful
mumps during pregnancy can lead to a miscarriage
meningitis which is swelling of the membranes around your spinal cord and brain
encephalitis which is is inflammation of the brain can cause seizures, severe headaches, and loss of consciousness
pancreatitis or inflammation of the pancreas leading to abdominal pain, nausea and vomiting
- damage to the cochlea in the inner ear causing loss of hearing
What is the treatment for mumps?
Antibiotics cannot help treat mumps as it is a virus. The doctor may prescribe fever reducers and painkillers to hasten the healing.
Patient Experiences



Questions answered by trusted doctors



Did you know?
Above 90% cases of mumps go unreported in India
More than 90% of the mumps cases in India go unreported.
Mumps during pregnancy can cause miscarriage
Mumps during pregnancy can be dangerous, with an increased risk of miscarriage within the first 12-16 weeks.
Sometimes mumps patients do not display any symptoms
Around 20% - 30% of the people do not have any symptoms and nearly 40% people have respiratory symptoms without infection in the salivary glands.
Related videos
Related articles
Pneumonia is an infection of the lungs caused by bacteria, viruses, or fungi. Know more about Pneumonia, its causes, symptoms, treatment and other useful facts and links and videos on Health-Wiki | Practo
Viral fever is characterized by high fever, burning in the eyes, headaches, body aches. Read about the symptoms, duration, causes and remedies of Viral Fever. Get information, videos and facts about Viral Fever on Health-Wiki | Practo
A surgical procedure in which either total or partial part of hip is replaced with artificial prosthesis is called as Hip Replacement.