Contents
In this article we will look at:
- What is hypothyroidism?
- How does hypothyroidism occur?
- Who is prone to hypothyroidism?
- What is the cause of hypothyroidism?
- What are the symptoms of hypothyroidism?
- How is hypothyroidism diagnosed?
- What are the complications of hypothyroidism?
- What is the treatment of hypothyroidism?
You can click on any of the links above to navigate to the section of your interest.
What is hypothyroidism?
Hypothyroidism is a condition in which the body’s thyroid gland is underactive. Meaning, the thyroid gland fails to produce enough of the thyroid hormones, Triiodothyronine (T3), and Thyroxine (T4).
The hormones produced by the thyroid gland affect the metabolism of the body. The hormones in general control how energy is used in your body and the resulting rate at which the different organs function in your body.
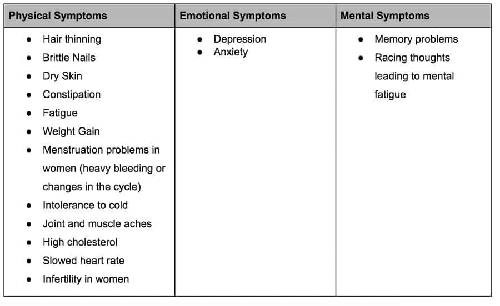
The classic symptoms of hypothyroidism are fatigue, a hoarse voice, weight gain, constipation, pain in the joints, thinning hair, joint aches, muscle stiffness, dry skin, and increased sensitivity to cold. You need to consult your family physician or a general physician immediately for a diagnosis. If you are diagnosed of hypothyroidism, your physician should be able to treat and monitor your condition. You can also meet an endocrinologist for the management of hypothyroidism. However, if your symptoms are more aggressive, he may refer you to an endocrinologist for specialized treatment.
How does hypothyroidism occur?
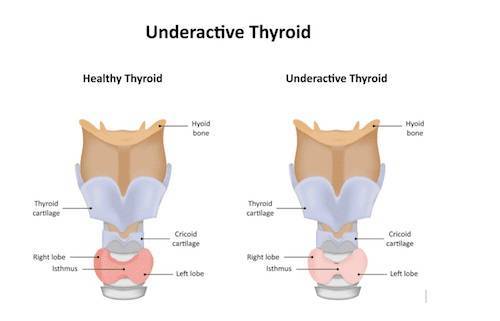
The thyroid gland is situated in front of the neck, below the voice box (larynx). It is a butterfly-shaped organ which has two lobes. The two lobes are on either side of the windpipe connected by a thin bridge (isthmus) of thyroid tissue.
The thyroid gland is a part of the endocrine system of the body, which consists of a collection of glands in the body and the hormones produced by those glands.
The hypothalamus located in the brain directly controls the production of thyroid hormone through the pituitary gland. It produces the thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH), which signals the pituitary gland to release a hormone called thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH). The TSH hormone released by the pituitary gland, in turn, signals the thyroid gland to produce the T3 or T4 hormones. If more T3 or T4 hormones are required, the pituitary gland produces more TSH and if the T3 and T4 levels are already high in the body, the pituitary gland releases less TSH.
Hypothyroidism occurs when the production of T3 and T4 hormones by the thyroid gland is too less for the body. This can slow down your metabolism, and growth rate.
Hypothyroidism may sometimes also lead to depression.
Who is prone to hypothyroidism?
Some people such as the following are more prone to hypothyroidism than others such as:
- people with a family history of hypothyroidism
- people with previous history of thyroid problems
- older people as the risk increases with age
- women
- people suffering from autoimmune disorders such as Diabetes Type 1, multiple sclerosis, rheumatoid arthritis, celiac disease, Addison's disease, pernicious anemia, or vitiligo
- people with down syndrome
- people with Turner syndrome
- people with bipolar disorder
What is the cause of hypothyroidism?
Hypothyroidism can be caused by a number of factors such as:
- Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis: This is a condition in which the thyroid gland gets inflamed. Also known as Thyroiditis, this occurs when the body’s immune system attacks the thyroid gland and destroys it.
- Iodine Deficiency: The thyroid gland needs iodine to be able to produce T3 and T4 hormones. Since our bodies do not produce iodine, we are dependent on the foods we consume to provide the required amount of iodine to the body. Foods that are rich in iodine include milk and milk-based products, saltwater fishes, eggs, bananas, yoghurt, strawberries, cranberries, green beans, and white bread.
- Pregnancy: During pregnancy, some women tend to develop an inflamed thyroid. This condition is also known as postpartum thyroiditis. Though the cause for it is unknown, after a certain time span, the thyroid hormone levels return to normal in these women.
- Radiation Therapy: Radiation given to the thyroid gland can reduce its production of hormones.
- Certain medications: Some medicines can interfere with normal production of thyroid hormone. Lithium, for example, is one of the most common medicines that causes hypothyroidism.
- Growths in the thyroid: Thyroid nodules are abnormal overgrowths of tissue in the thyroid gland that are most often benign—but may be cancerous in some people. There are a few disorders that can cause these growths an example of which is the autoimmune disorder known as sarcoidosis. In sarcoidosis, inflamed tissue forms throughout the body. The inflamed tissue replaces the healthy thyroid tissue, which results in inhibiting thyroid hormone production. As a result, hypothyroidism occurs.
- Genetic Causes: Damaged genes can also cause hypothyroidism. The causes are generally detected during infancy.
- Problem With The Hypothalamus: Hypothalamic dysfunction caused by surgery, traumatic brain injury, tumours, and radiation can, in turn, can cause hypothyroidism. The hypothalamus controls the pituitary gland, which in turn controls the thyroid gland among others. Therefore, any abnormality in the hypothalamus can cause the thyroid gland to dysfunction.
- Pituitary Gland Disorder: The pituitary gland turn controls the thyroid gland among others. Therefore, any abnormal functioning of the pituitary gland affects the thyroid gland.
What are the symptoms of hypothyroidism? How is hypothyroidism diagnosed?
The symptoms or signs of hypothyroidism include:
Diagnosis
A general practitioner can diagnose and treat hypothyroidism. For severe cases, an endocrinologist (a doctor who specializes in the endocrine system, which includes the body’s hormone-secreting glands, such as the thyroid) can be consulted.
Hypothyroidism can be detected by specific blood tests, i.e.TSH and T4 (thyroxine) Test.
What are the complications of hypothyroidism?
The complications of hypothyroidism include:
- Rapid ageing
- Dry skin and wrinkles
- Prematurely greying hair
- Infertility in women
- Cardiac complications
- Nerve damage
- Renal complications
- Pregnancy-related complications
- Myxedema (a life-threatening form of hypothyroidism which can cause death)
- Obesity
What is the treatment of hypothyroidism?
Medical Treatment
Your doctor will prescribe certain medications which will help reduce your hypothyroidism symptoms. He may also suggest some supplements as well changes in the diet.
Exercise
Following the right exercise regimen can help reduce your hypothyroidism symptoms.
Performing low-impact aerobic exercises can get your heart rate up and your lungs going without putting too much pressure on your joints. This is important because joint pain is a common hypothyroidism symptom.
Strength training exercises such as lunges, leg raises, and push-ups or those involving weight-training machines can build muscle mass, and muscle burns more calories than fat, even when you're at rest. Building muscle can help counter possible weight gain from an underactive thyroid.
Pilates or gentle yoga can improve your core muscles and ease back and hip pain associated with hypothyroidism.
Walking is an immensely beneficial exercise as well.
Patient Experiences



Questions answered by trusted doctors


Did you know?
42 Million in India suffer from thyroid problems
Approximately 42 million people in India suffer from thyroid diseases.
Women Are More Prone
Hypothyroidism is about eight to 10 times less common in men than in women. It is an autoimmune disorder which are more common among women.
Older People Are More Prone
Hypothyroidism affects 10.95% of the studied population in India.The older population (above the age of 35 years) are at a higher risk of hypothyroidism than the younger population.
Related videos
Related articles
Dialysis is a procedure in which the blood is filtered mechanically without the help of the kidneys. If the kidneys are not functioning properly then Dialysis will take over the function of the failed kidneys.
Breast cancer occurs when healthy cells of breast tissue change and may begin to grow out of control which can appear as a lump within breast tissue. Breast Cancer Treatment includes chemotherapy, radiotherapy,surgery depend on the type of cancer.
The treatment method of using various treatments like chemotherapy, radiation, anti-cancer drugs to either cure, treat, control, or reduce the symptoms of any types of cancer can be grouped together as cancer treatments.



