
Contents
In this article, we will look at:
- What is dyspareunia?
- What are the causes of dyspareunia?
- Symptoms of dyspareunia
- Diagnosis of dyspareunia
- Complications of dyspareunia
- Treatment for dyspareunia
- Exercising for Managing Dyspareunia
You can click on any of the links above to navigate to the section of your interest.
What is dyspareunia?
The word dyspareunia is derived from the Greek language, and the meanings include "difficulty in mating" or "badly mated."
Dyspareunia or pain during sexual intercourse can occur both in men and women but is more common among women. The pain can range from moderate to severe and occurs in a woman's labial or vulvar areas, during or immediately after sex. The pain may also be experienced as a pelvic pain or vaginal pain and is often accompanied by a burning or throbbing sensation.
What are the causes of dyspareunia?
There are a variety of causes that can lead to dyspareunia:
- Psychological
- Medical factors
- Other causes
The psychological causes include:
- Depression, fear, and anxiety which can affect sexual arousal and lead to conditions such as vaginismus, or vaginal dryness
- A history of sexual abuse or trauma
- Stress
- Domestic violence
The medical factors that can lead to dyspareunia include:
- Atrophic vaginitis or vaginal atrophy which is a common condition that causes thinning, drying or inflammation of the vaginal lining in postmenopausal women
- Urinary tract infections, vaginal yeast infections, or sexually transmitted diseases like candida, herpes simplex or genital warts
- Skin disease, such as psoriasis or lichen sclerosus.
- Cystitis or inflammation of the bladder wall caused by a bacterial infection
- Endometriosis a painful gynaecological condition, which occurs in women when the tissue that makes up the uterus lining develops elsewhere in the body.
- Fibroids which are often benign tumours that grow on the wall of the uterus
- Interstitial cystitis which is a chronic painful bladder condition
- Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) which is a functional disorder of the digestive tract
- Ovarian cysts a condition where a build-up of fluid within an ovary occurs
- Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) which causes inflammation of the female reproductive organs, usually caused by infection
- Uterine prolapse a condition in which one or more pelvic organs extend into the vagina
The other causes that can lead to dyspareunia include:
- Side effects of some drugs
- Allergic reaction to clothing, or spermicides
What are the symptoms of dyspareunia? How is dyspareunia diagnosed?
The symptoms of dyspareunia include:
- Lack of sexual desire
- Inability to get aroused
- Pain that occurs only during sexual penetration
- Repeatedly experiencing pain while the partner thrusts
- Burning sensation along with the pain
- Inability to experience orgasm
- Pain while inserting a tampon
- Throbbing or burning sensation which occurs with the pain and lasts for a long time after the intercourse
Diagnosis
A medical evaluation for dyspareunia includes:
- The doctor asking in detail about your sexual history, medical and surgical history, when did your pain begin, whether it occurs in certain sexual positions. In case of multiple sex partners, the patient needs to mention if the pain occurs only with certain partners.
- A pelvic exam by the doctor to check for any form of infections. During the pelvic exam, the doctor may apply gentle pressure on the genital muscles with a cotton swab to identify the location of the pain.
- Based on the physical exam the doctor may recommend
- a pelvic ultrasound
- a visual exam of the vagina, using an instrument called a speculum
What are the complications of dyspareunia?
Dyspareunia does not usually cause any form of severe health complications. However, it can affect the sexual life of the person. With the right intervention and treatment, dyspareunia can be managed and even cured.
What is the treatment for dyspareunia?
Medical Treatment for Dyspareunia
The treatment of dyspareunia varies according to the cause:
- In case of dyspareunia which is caused by vaginal dryness, the doctor prescribes vaginal lubricants and may also suggest adequate foreplay.
- In case of infections and sexually transmitted diseases, the doctor will prescribe antibiotics.
- In case of allergies, the doctor may prescribe topical creams.
- For women suffering from dyspareunia due to hormonal problems, hormonal therapy may be prescribed.
- Surgical intervention may be required for women suffering from problems such as abnormal endometrial tissue growth or uterine fibroids.
- Psychological counselling may be required for women who have suffered from sexual abuse and trauma.
Exercising for Managing Dyspareunia
Stretch exercises which strengthen the pelvic floor can help immensely in doing away with the symptoms of dyspareunia. Practicing yoga regularly can help in strengthening and removing the tightness of muscles that can cause the pain associated with dyspareunia. Yoga can also decrease stress levels, anxiety, depression and boost your self-image and self-confidence.
Doing The Kegel Exercise
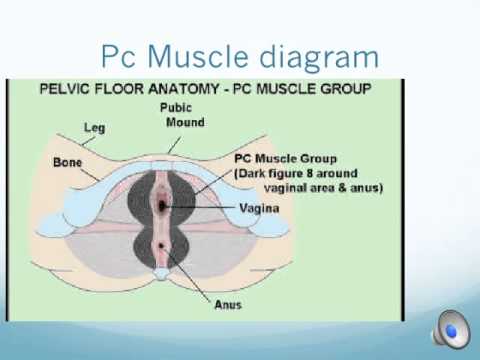
Doing the Kegel exercise can help with the symptoms of dyspareunia. The Kegel exercise was named after Dr. Arnold Kegel, who has popularized them in the ‘50s.This exercise initially was meant to cure patients suffering from urinary incontinence (often after childbirth).
Gradually the efficacy of Kegel’s exercise was discovered for patients who suffer from conditions like dyspareunia and vaginismus.
You can easily identify the vaginal muscles which play an active part during sex with this simple exercise.
Go to the bathroom and urinate a little, then stop the flow of your urine. Then start urinating again, retain the flow of urine, and stop again and then start again. Do so until you have emptied your bladder.
The muscles which just acted according to your wishes are the same ones involved in dilating and contracting during sex especially during vaginal penetration.
Once you identify these muscles it is important to exercise them in order to be able to contract and relax these muscles at will. This will help you gain control over the vaginal muscles keeping pain at bay during sexual penetration. This is known as Kegel’s exercise.
The exercise of alternatively stopping and letting the urine flow is only for test purposes to identify the muscles which need to be exercised while performing the Kegel's exercises.
Warning: Please do not do the Kegel exercise while urinating. When you are still at the stage of practicing the Kegel exercise, do not attempt a sexual intercourse with penetration.
The Kegel Exercise
Practice the Kegel exercise for a week or two.
Find a quiet suitable place to do the exercise. You can do it after waking up in the morning and just before bedtime while lying on your bed.
Follow the steps given below:
- Contract your pelvic muscles. Squeeze and hold for 3 seconds
- Then relax for another 3 seconds.
- Repeat the exercise for as many as 10 times each session, until you can do around 15 repetitions.
Initially, a certain effort of concentration will be needed to contract the pelvic muscles only, without contracting the abdominal and gluteal muscles. When you get used to it, it will become automatic.
Once you become comfortable doing these sessions quietly in bed, you can do the Kegel exercises anytime while doing some other activities for example, watching TV, working on your computer, in your car, etc.
Syncing the Kegel Exercises with Breathing Exercises
Once you are comfortable doing Kegel’s exercise anywhere, sync it with breathing exercises:
- Focus on your breathing for a few minutes. Breathe in and out deeply a couple of times to relax yourself.
- Then inhale deeply and hold your breath for a few seconds while strongly contracting your pelvic floor muscles.
- Then exhale deeply and relax these muscles.
Repeat several series of this exercise.
You can do this exercise in front of a mirror in order to visualize your vaginal muscles at work. This can immensely help to improve your mental awareness of this part of your body and help boost your performance when you resume your sex life.
Questions answered by trusted doctors

Did you know?
Dyspareunia in Women
Dyspareunia affects 8 - 22% of females, making it a very frequent issue in gynecologic practice. Even without this disorder a significant proportion of women – between 6.5% and 15% – experience varying levels of pain in their genital areas particularly during sexual intercourse at some point in their life.
Dyspareunia in India
Dyspareunia is 12.6%, with a higher prevalence in the central region of India, among newly married and younger women. It is more prevalent.
Related videos
Related articles
Monthly periods, or menstruation or the menstrual cycle is body’s way of preparing for pregnancy each month in a woman. It is when the body sheds the lining of the uterus and the menstrual blood flows from the uterus through the cervix and the vagina and
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) is a common endocrine disorder among women of child-bearing age. Know more about the symptoms, treatment, cure, and remedies of PCOS. Get information, videos and facts about PCOS on Health-Wiki | Practo
This is a minimally invasive surgical procedure using a laparoscope to remove the uterus and/or fallopian tubes and ovaries through the vagina.


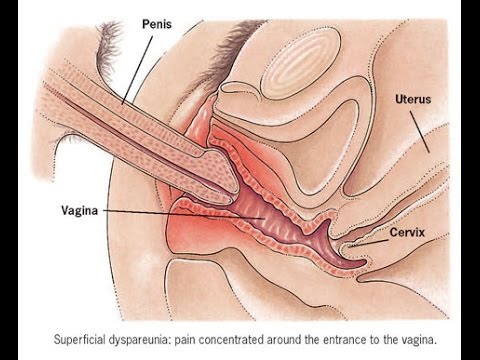


Poor hygiene and less lubrication cn also be one of the reasons..